Interleukin-12 drives the Th1 signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa
- PMID: 17220306
- PMCID: PMC1865692
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01446-06
Interleukin-12 drives the Th1 signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa
Abstract
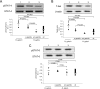
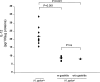
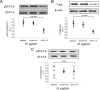
In this study we examined mechanisms that regulate T-helper lymphocyte 1 (Th1) commitment in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. The levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), interleukin-4 (IL-4), and IL-12 in total extracts of gastric biopsies taken from H. pylori-infected and uninfected patients were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4), STAT6, and T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet) in total proteins extracted from gastric biopsies were determined by Western blotting. Finally, the effect of a neutralizing IL-12 antibody on expression of Th1 transcription factors and the levels of IFN-gamma in organ cultures of H. pylori-infected biopsies was examined. Increased levels of IFN-gamma and IL-12 were found in gastric biopsy samples of H. pylori-infected patients compared to the levels in uninfected patients. In addition, H. pylori-infected biopsies exhibited high levels of expression of phosphorylated STAT4 and T-bet. Higher levels of IFN-gamma and expression of Th1 transcription factors were associated with greater infiltration of mononuclear cells in the gastric mucosa. By contrast, production of IL-4 and expression of phosphorylated STAT6 were not associated with the intensity of mononuclear cell infiltration. In ex vivo organ cultures of H. pylori-infected biopsies, neutralization of endogenous IL-12 down-regulated the expression of phosphorylated STAT4 and T-bet and reduced IFN-gamma production. Our data indicated that IL-12 contributes to the Th1 cell commitment in H. pylori-infected human gastric mucosa.
Figures
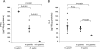

Similar articles
-
Enhanced activation of cyclooxygenase-2 downregulates Th1 signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa.Helicobacter. 2007 Jun;12(3):193-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00498.x. Helicobacter. 2007. PMID: 17492998
-
Enhanced expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa modulates Th1/Th2 pathway and interleukin 17 production.Helicobacter. 2015 Feb;20(1):41-8. doi: 10.1111/hel.12174. Epub 2014 Oct 11. Helicobacter. 2015. PMID: 25308308
-
gammadelta T cells increase with gastric mucosal interleukin (IL)-7, IL-1beta, and Helicobacter pylori urease specific immunoglobulin levels via CCR2 upregulation in Helicobacter pylori gastritis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Jan;21(1 Pt 1):32-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04148.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16706809
-
Dendritic cell function in the host response to Helicobacter pylori infection of the gastric mucosa.Pathog Dis. 2013 Feb;67(1):46-53. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12014. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Pathog Dis. 2013. PMID: 23620119 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastric inflammation.Br Med Bull. 1998;54(1):139-50. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a011664. Br Med Bull. 1998. PMID: 9604438 Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of Th2 Immune Responses in Mediating the Progression of Gastritis-Associated Metaplasia to Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 25;16(3):522. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030522. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-γ-producing B cells induce the formation of gastric lymphoid follicles after Helicobacter suis infection.Mucosal Immunol. 2015 Mar;8(2):279-95. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.66. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Mucosal Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25073677
-
The TLR/MyD88 signalling cascade in inflammation and gastric cancer: the immune regulatory network of Helicobacter pylori.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Jul;101(7):767-781. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02332-5. Epub 2023 May 17. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37195446 Review.
-
Cytotoxic T cells in H. pylori-related gastric autoimmunity and gastric lymphoma.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:104918. doi: 10.1155/2010/104918. Epub 2010 Jun 22. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20617132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-γ promotes gastric lymphoid follicle formation but not gastritis in Helicobacter-infected BALB/c mice.Gut Pathog. 2016 Nov 21;8:61. doi: 10.1186/s13099-016-0142-0. eCollection 2016. Gut Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27895717 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

