Long-term treatment with TGFbeta1 impairs mechanotransduction in bovine aortic endothelial cells
- PMID: 17220908
- PMCID: PMC2189726
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707123
Long-term treatment with TGFbeta1 impairs mechanotransduction in bovine aortic endothelial cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Vascular endothelial cells play a role in the physiological response to mechanical stress. Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) induces morphological changes in endothelial cells, and this may alter their mechanosensitive responses. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of TGFbeta1 on hypotonic stress (HTS)-induced responses in bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs).
Experimental approach: Cultured BAECs were treated with 3 ng ml(-1) TGFbeta1 for 24 h (24h-TGFbeta1) or 7 days (7d-TGFbeta1). Cytosolic actin fibres were stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. Intracellular Ca2+ concentration was measured using fura2. Tyrosine phosphorylation and RhoA expression were assessed by Western blotting. Expression of RhoA mRNA was assessed by real-time PCR.
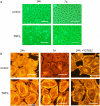
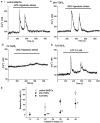
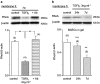
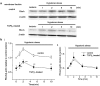
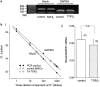
Key results: BAECs developed pseudopod-like processes within 24 h and showed a fibroblast-like appearance after 7 days. HTS induced Ca2+ transients via endogenous ATP release in both control and 24h-TGFbeta1 BAECs but not in 7d-TGFbeta1 BAECs. We have previously shown that HTS-induced ATP release is mediated by sequential activation of RhoA and tyrosine kinases. The basal amount of membrane-bound RhoA was significantly lower in 7d-TGFbeta1 than in 24h-TGFbeta1 or control BAECs. HTS increased the membrane-bound RhoA to the same fractional level in 24h-TGFbeta1 and control BAECs, but its net maximal amount was significantly lower in 7d-TGFbeta1. HTS-induced downstream signals of RhoA activation, i.e. the tyrosine phosphorylation of FAK and paxillin, were markedly suppressed in 7d-TGFbeta1 BAECs.
Conclusions and implications: These results indicate that long-term treatment with TGFbeta1 does not impair mechanoreception in BAECs but impairs mechanotransduction by affecting RhoA membrane translocation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sustained contraction and loss of NO production in TGFbeta1-treated endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;149(4):355-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706883. Epub 2006 Sep 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16967050 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of heparan sulfate proteoglycan in sensing hypotonic stress in bovine aortic endothelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1780(10):1148-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.07.004. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18680786
-
Sequential activation of RhoA and FAK/paxillin leads to ATP release and actin reorganization in human endothelium.J Physiol. 2004 Jul 15;558(Pt 2):479-88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.065334. Epub 2004 May 21. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15155793 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Rho-kinase and tyrosine kinase in hypotonic stress-induced ATP release in bovine aortic endothelial cells.J Physiol. 2001 May 1;532(Pt 3):759-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0759e.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11313444 Free PMC article.
-
[ATP release pathways in vascular endothelial cells].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004 Jun;123(6):403-11. doi: 10.1254/fpj.123.403. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15170080 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Arciniegas E, Sutton AB, Allen TD, Schor AM. Transforming growth factor β1 promotes the differentiation of endothelial cells into smooth muscle-like cells in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1992;103:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Ren S, Ma MG, Dharmalingam S, Lu L, Xue M, et al. Hirulog-like peptide reduces restenosis and expression of tissue factor and transforming growth factor-β in carotid artery of atherosclerotic rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 2003;169:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Clements RT, Minnear FL, Singer HA, Keller RS, Vincent PA. RhoA and Rho-kinase dependent and independent signals mediate TGF-β-induced pulmonary endothelial cytoskeletal reorganization and permeability. Am J Physiol. 2005;288:L294–L306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

