Matrix metalloproteinase-7-catalyzed release of HB-EGF mediates deoxycholyltaurine-induced proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line
- PMID: 17222808
- PMCID: PMC1852457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.11.028
Matrix metalloproteinase-7-catalyzed release of HB-EGF mediates deoxycholyltaurine-induced proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line
Abstract
Prior evidence indicates that bile acids stimulate colon cancer cell proliferation by muscarinic receptor-induced transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR). To explore further the mechanism underlying this action, we tested the hypothesis that bile acids activate a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) that catalyzes release of an EGFR ligand. Initial studies showed that non-selective MMP inhibitors blocked the actions of deoxycholyltaurine (DCT), thereby indicating a role for MMP-catalyzed release of an EGFR ligand. DCT-induced cell proliferation was reduced by increasing concentrations of EGFR kinase inhibitors, by antibodies to the ligand binding domain of EGFR, by neutralizing antibodies to heparin binding-EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and by CRM197, an inhibitor of HB-EGF release. These findings and our observations with more selective MMP inhibitors suggested that MMP-7, an enzyme known to release HB-EGF, plays a key role in mediating bile acid-induced H508 colon cancer cell proliferation. We observed that recombinant HB-EGF and MMP-7 mimicked both the signaling and proliferative actions of bile acids. Strikingly, reducing MMP-7 expression with either neutralizing antibody or small interfering RNA attenuated the actions of DCT. MMP-7 expression in H508 cells was confirmed using quantitative reverse transcription PCR. DCT stimulated a greater than 10-fold increase in MMP-7 gene transcription. Co-localization of pro-MMP-7 and pro-HB-EGF at the cell surface (immunofluorescence microscopy) was demonstrated, indicating proximity of the enzyme to its substrate. These findings provide strong evidence that in H508 human colon cancer cells, DCT-induced transactivation of EGFR is mediated by MMP-7-catalyzed release of the EGFR ligand HB-EGF.
Figures

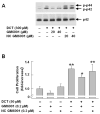


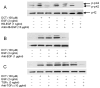









References
-
- Hill MJ. Bile acids and colorectal cancer: hypothesis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1991;1:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Reddy BS, Wynder EL. Metabolic epidemiology of colon cancer. Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in colon cancer patients and patients with adenomatous polyps. Cancer. 1977;39:2533–9. - PubMed
-
- Glinghammar B, Rafter J. Carcinogenesis in the colon: interaction between luminal factors and genetic factors. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1999;8:S87–S94. - PubMed
-
- Narisawa T, Magadia NE, Weisburger JH, Wynder EL. Promoting effect of bile acids on colon carcinogenesis after intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats. J Natl Cancer Instit. 1974;53:1093–7. - PubMed
-
- Reddy BS, Narasawa T, Weisburger JH, Wynder EL. Promoting effect of sodium deoxycholate on colon adenocarcinomas in germfree rats. J Natl Cancer Instit. 1976;56:441–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

