Relationships between the sequence of alpha-synuclein and its membrane affinity, fibrillization propensity, and yeast toxicity
- PMID: 17222866
- PMCID: PMC1868670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.044
Relationships between the sequence of alpha-synuclein and its membrane affinity, fibrillization propensity, and yeast toxicity
Abstract
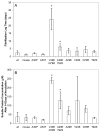
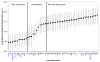
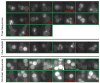
To investigate the alpha-synuclein protein and its role in Parkinson's disease, we screened a library of random point mutants both in vitro and in yeast to find variants in an unbiased way that could help us understand the sequence-phenotype relationship. We developed a rapid purification method that allowed us to screen 59 synuclein mutants in vitro and discovered two double-point mutants that fibrillized slowly relative to wild-type, A30P, and A53T alpha-synucleins. The yeast toxicity of all of these proteins was measured, and we found no correlation with fibrillization rate, suggesting that fibrillization is not necessary for synuclein-induced yeast toxicity. We found that beta-synuclein was of intermediate toxicity to yeast, and gamma-synuclein was non-toxic. Co-expression of Parkinson's disease-related genes DJ-1, parkin, Pink1, UCH-L1, or synphilin, with synuclein, did not affect synuclein toxicity. A second screen, of several thousand library clones in yeast, identified 25 non-toxic alpha-synuclein sequence variants. Most of these contained a mutation to either proline or glutamic acid that caused a defect in membrane binding. We hypothesize that yeast toxicity is caused by synuclein binding directly to membranes at levels sufficient to non-specifically disrupt homeostasis.
Figures



References
-
- Cookson MR. The biochemistry of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:29–52. - PubMed
-
- Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT., Jr Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 1998;4:1318–20. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388:839–40. - PubMed
-
- Davidson WS, Jonas A, Clayton DF, George JM. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:9443–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

