Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update
- PMID: 17223625
- PMCID: PMC1797635
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00027-06
Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update
Abstract
Infection with Histoplasma capsulatum occurs commonly in areas in the Midwestern United States and Central America, but symptomatic disease requiring medical care is manifest in very few patients. The extent of disease depends on the number of conidia inhaled and the function of the host's cellular immune system. Pulmonary infection is the primary manifestation of histoplasmosis, varying from mild pneumonitis to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. In those with emphysema, a chronic progressive form of histoplasmosis can ensue. Dissemination of H. capsulatum within macrophages is common and becomes symptomatic primarily in patients with defects in cellular immunity. The spectrum of disseminated infection includes acute, severe, life-threatening sepsis and chronic, slowly progressive infection. Diagnostic accuracy has improved greatly with the use of an assay for Histoplasma antigen in the urine; serology remains useful for certain forms of histoplasmosis, and culture is the ultimate confirming diagnostic test. Classically, histoplasmosis has been treated with long courses of amphotericin B. Today, amphotericin B is rarely used except for severe infection and then only for a few weeks, followed by azole therapy. Itraconazole is the azole of choice following initial amphotericin B treatment and for primary treatment of mild to moderate histoplasmosis.
Figures
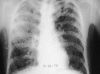

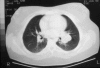
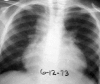


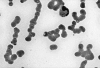
References
-
- Bamberger, D. M. 1999. Successful treatment of multiple cerebral histoplasmomas with itraconazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28:915-916. - PubMed
-
- Bhatti, S., L. Vilenski, R. Tight, and R. A. Smego, Jr. 2004. Histoplasma endocarditis: clinical and mycologic features and outcomes. J. Infect. 51:2-9. - PubMed
-
- Bialek, R., F. Ernst, K. Dietz, L. K. Najvar, J. Knobloch, J. R. Graybill, and G. Schaumburg-Lever. 2002. Comparison of staining methods and a nested PCR assay to detect Histoplasma capsulatum in tissue sections. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 117:597-603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

