Predominant activation of MAP kinases and pro-destructive/pro-inflammatory features by TNF alpha in early-passage synovial fibroblasts via TNF receptor-1: failure of p38 inhibition to suppress matrix metalloproteinase-1 in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17223661
- PMCID: PMC1954705
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.062521
Predominant activation of MAP kinases and pro-destructive/pro-inflammatory features by TNF alpha in early-passage synovial fibroblasts via TNF receptor-1: failure of p38 inhibition to suppress matrix metalloproteinase-1 in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To examine the relative importance of tumour necrosis factor-receptor 1 (TNF-R1) and TNF-R2 and their signalling pathways for pro-inflammatory and pro-destructive features of early-passage synovial fibroblasts (SFB) from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods: Cells were stimulated with tumour necrosis factor (TNF)alpha or agonistic anti-TNF-R1/TNF-R2 monoclonal antibodies. Phosphorylation of p38, ERK and JNK kinases was assessed by western blot; proliferation by bromodesoxyuridine incorporation; interleukin (IL)6, IL8, prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 secretion by ELISA; and MMP-3 secretion by western blot. Functional assays were performed with or without inhibition of p38 (SB203580), ERK (U0126) or JNK (SP600125).
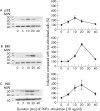
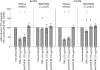
Results: In RA- and OA-SFB, TNFalpha-induced phosphorylation of p38, ERK or JNK was exclusively mediated by TNF-R1. Reduction of proliferation and induction of IL6, IL8 and MMP-1 were solely mediated by TNF-R1, whereas PGE(2) and MMP-3 secretion was mediated by both TNF-Rs. In general, inhibition of ERK or JNK did not significantly alter the TNFalpha influence on these effector molecules. In contrast, inhibition of p38 reversed TNFalpha effects on proliferation and IL6/PGE(2) secretion (but not on IL8 and MMP-3 secretion). The above effects were comparable in RA- and OA-SFB, except that TNFalpha-induced MMP-1 secretion was reversed by p38 inhibition only in OA-SFB.
Conclusion: In early-passage RA/OA-SFB, activation of MAPK cascades and pro-inflammatory/pro-destructive features by TNFalpha is predominantly mediated by TNF-R1 and, for proliferation and IL6/PGE(2) secretion, exclusively regulated by p38. Strikingly, RA-SFB are insensitive to p38 inhibition of MMP-1 secretion. This indicates a resistance of RA-SFB to the inhibition of pro-destructive functions and suggests underlying structural/functional alterations of the p38 pathway, which may contribute to the pathogenesis or therapeutic sensitivity of RA, or both.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Similar articles
-
Preferential induction of prodestructive matrix metalloproteinase-1 and proinflammatory interleukin 6 and prostaglandin E2 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via tumor necrosis factor receptor-55.J Rheumatol. 2003 Aug;30(8):1680-90. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12913922
-
p38 inhibition and not MK2 inhibition enhances the secretion of chemokines from TNF-α activated rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;31(4):515-25. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23558031
-
Annexin-1 mediates TNF-alpha-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase secretion from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 15;181(4):2813-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2813. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18684973
-
TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways.Semin Immunol. 2014 Jun;26(3):237-45. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24647229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the role of p38 MAP kinase in growth of Werner syndrome fibroblasts.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jun;1197:45-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05195.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20536832 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Frequency Vibration Promotes Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Production to Increase Cartilage Degeneration in Knee Osteoarthritis.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(2_suppl):1398S-1406S. doi: 10.1177/1947603520931178. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 32532183 Free PMC article.
-
TNF in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: friend or foe?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Apr;17(4):213-223. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00584-4. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33686279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Death-associated protein kinase controls STAT3 activity in intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Pathol. 2013 Mar;182(3):1005-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.11.026. Am J Pathol. 2013. Retraction in: Am J Pathol. 2017 Jan;187(1):225. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.09.019. PMID: 23438478 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Inhibition of inflammatory mediators and related signaling pathways by macrophage-stimulating protein in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Inflamm Res. 2011 Sep;60(9):823-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0338-1. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21528357
-
The inhibition of Src kinase suppresses the production of matrix metalloproteinases in from synovial fibroblasts and inhibits MAPK and STATs pathways.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Aug 30;51(4):2142-2149. doi: 10.3906/sag-2008-274. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33714238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Firestein G S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003423356–361. - PubMed
-
- Yamanishi Y, Firestein G S. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: the role of synoviocytes. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 200127355–371. - PubMed
-
- Chomarat P, Rissoan M C, Pin J J, Banchereau J, Miossec P. Contribution of IL‐1, CD14, and CD13 in the increased IL‐6 production induced by in vitro monocyte‐synoviocyte interactions. J Immunol 19951553645–3652. - PubMed
-
- Gay S. Rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 200113191–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous