Pseudomonas aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB stimulate ABCA1-mediated phospholipid efflux via ERK-activation of PPARalpha-RXR
- PMID: 17223797
- PMCID: PMC1876365
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061364
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB stimulate ABCA1-mediated phospholipid efflux via ERK-activation of PPARalpha-RXR
Abstract
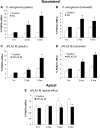
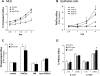
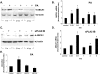
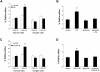
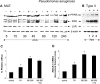
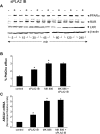
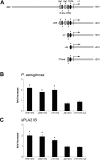
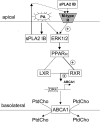
Bacterial infection triggers an acute inflammatory response that might alter phospholipid metabolism. We have investigated the acute-phase response of murine lung epithelia to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Ps. aeruginosa triggered secretion of the pro-inflammatory lipase, sPLA2 IB (phospholipase A2 IB), from lung epithelium. Ps. aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB each stimulated basolateral PtdCho (phosphatidylcholine) efflux in lung epithelial cells. Pre-treatment of cells with glyburide, an inhibitor of the lipid-export pump, ABCA1 (ATP-binding cassette transporter A1), attenuated Ps. aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB stimulation of PtdCho efflux. Effects of Ps. aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB were completely abolished in human Tangier disease fibroblasts, cells that harbour an ABCA1 genetic defect. Ps. aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB induced the heterodimeric receptors, PPARa (peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor-a) and RXR (retinoid X receptor), factors known to modulate ABCA1 gene expression. Ps. aeruginosa and sPLA2 IB stimulation of PtdCho efflux was blocked with PD98059, a p44/42 kinase inhibitor. Transfection with MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-signal-regulated kinase kinase 1), a kinase upstream of p44/42, increased PPARa and RXR expression co-ordinately with increased ABCA1 protein. These results suggest that pro-inflammatory effects of Ps. aeruginosa involve release of an sPLA2 of epithelial origin that, in part, via distinct signalling molecules, transactivates the ABCA1 gene, leading to export of phospholipid.
Figures
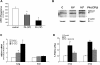
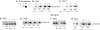
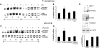
References
-
- Hauser A. R., Cobb E., Bodi M., Mariscal D., Valles J., Engel J. N., Rello J. Type III protein secretion is associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crit. Care Med. 2002;30:521–528. - PubMed
-
- Arbibe L., Vial D., Rosinski-Chupin I., Havet N., Huerre M., Vargaftig B. B., Touqui L. Endotoxin induces expression of type II phospholipase A2 in macrophages during acute lung injury in guinea pigs: involvement of TNF-α in lipopolysaccharide-induced type II phospholipase A2 synthesis. J. Immunol. 1997;159:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Vial D., Senorale-Pose M., Havet N., Molio L., Vargaftig B. B., Touqui L. Expression of the type-II phospholipase A2 in alveolar macrophages: down-regulation by an inflammatory signal. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:17327–17332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

