Differential effects of AT1 receptor and Ca2+ channel blockade on atherosclerosis, inflammatory gene expression, and production of reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 17224157
- PMCID: PMC2141541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.11.030
Differential effects of AT1 receptor and Ca2+ channel blockade on atherosclerosis, inflammatory gene expression, and production of reactive oxygen species
Abstract
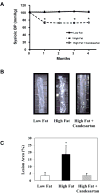
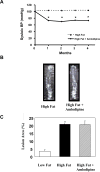
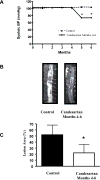
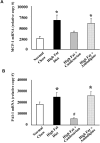
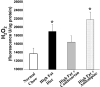
Angiotensin II receptor blockade has been shown to inhibit atherosclerosis in several different animal models. We sought to determine if this effect was the result of blood pressure reduction per se or a result of the anti-inflammatory effects of receptor blockade. ApoE-deficient mice were fed a high fat diet and treated with either an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, candesartan (0.5 mg/kg/day, s.c.) or a calcium channel blocker, amlodipine (7.5 mg/kg/day, mixed with food). Atherosclerotic lesion area, aortic inflammatory gene expression as well as aortic H2O2 and superoxide production were assayed. We found that candesartan but not amlodipine treatment dramatically attenuated the development of atherosclerosis despite a similar reduction in blood pressure. Similarly, candesartan treatment inhibited aortic expression of inflammatory genes and production of reactive oxygen species, effects not seen with amlodipine. These data demonstrate that angiotensin II receptor blockade inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing vascular oxidative stress and inflammatory gene production independent of blood pressure reduction.
Figures

References
-
- Weiss D, Sorescu D, Taylor WR. Angiotensin II and atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 2001;87:25C–32C. - PubMed
-
- Weiss D, Kools JJ, Taylor WR. Angiotensin II-induced hypertension accelerates the development of atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. Circulation. 2001;103:448–454. - PubMed
-
- Daugherty A, Cassis L. Chronic angiotensin II infusion promotes atherogenesis in low density lipoprotein receptor -/- mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;892:108–118. - PubMed
-
- Ihara M, Urata H, Kinoshita A, Suzumiya J, Sasaguri M, Kikuchi M, Ideishi M, Arakawa K. Increased chymase-dependent angiotensin II formation in human atherosclerotic aorta. Hypertension. 1999;33:1399–1405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

