Global genome expression analysis of rice in response to drought and high-salinity stresses in shoot, flag leaf, and panicle
- PMID: 17225073
- PMCID: PMC1805039
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-006-9111-1
Global genome expression analysis of rice in response to drought and high-salinity stresses in shoot, flag leaf, and panicle
Abstract
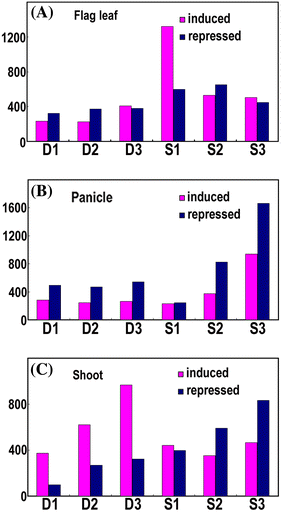
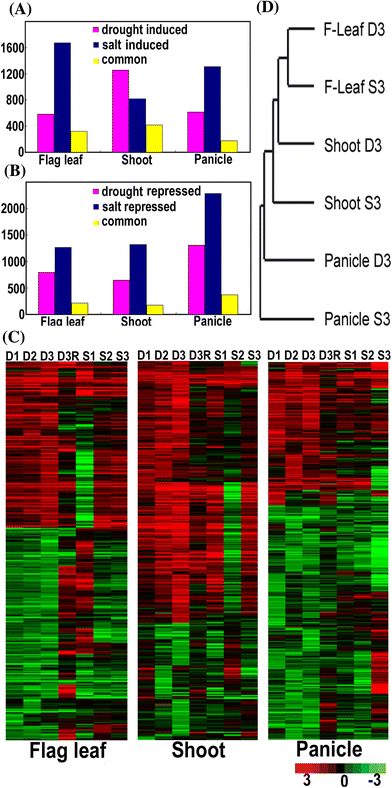
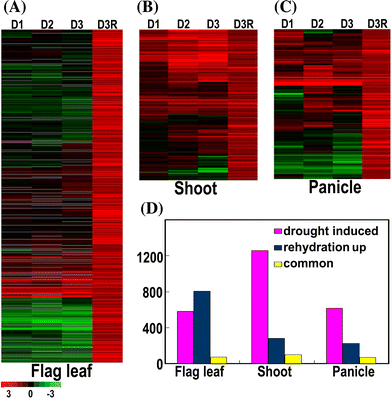
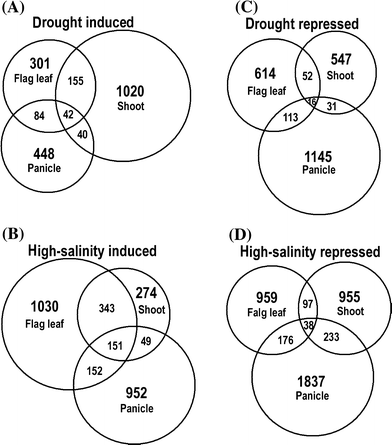
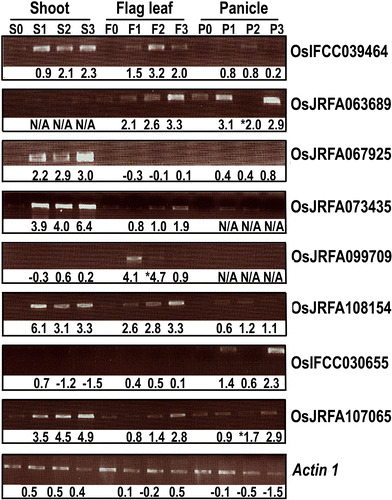
To elucidate genome-level responses to drought and high-salinity stress in rice, a 70 mer oligomer microarray covering 36,926 unique genes or gene models was used to profile genome expression changes in rice shoot, flag leaf and panicle under drought or high-salinity conditions. While patterns of gene expression in response to drought or high-salinity stress within a particular organ type showed significant overlap, comparison of expression profiles among different organs showed largely organ-specific patterns of regulation. Moreover, both stresses appear to alter the expression patterns of a significant number of genes involved in transcription and cell signaling in a largely organ-specific manner. The promoter regions of genes induced by both stresses or induced by one stress in more than one organ types possess relative enrichment of two cis-elements (ABRE core and DRE core) known to be associated with water stress. An initial computational analysis indicated that novel promoter motifs are present in the promoters of genes involved in rehydration after drought. This analysis suggested that rice might possess a mechanism that actively detects rehydration and facilitates rapid recovery. Overall, our data supports a notion that organ-specific gene regulation in response to the two abiotic stresses may primarily be mediated by organ-specific transcription responses.
Figures



References
-
- Barr HD, Weatherley PE (1962) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (2000) The adaptive control of the false discovery rate in multiple hypotheses testing. J Behav Educ Statist 25:60–83 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

