The origins of concentric demyelination: self-organization in the human brain
- PMID: 17225855
- PMCID: PMC1764710
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000150
The origins of concentric demyelination: self-organization in the human brain
Abstract
Baló's concentric sclerosis is a rare atypical form of multiple sclerosis characterized by striking concentric demyelination patterns. We propose a robust mathematical model for Baló's sclerosis, sharing common molecular and cellular mechanisms with multiple sclerosis. A reconsideration of the analogies between Baló's sclerosis and the Liesegang periodic precipitation phenomenon led us to propose a chemotactic cellular model for this disease. Rings of demyelination appear as a result of self-organization processes, and closely mimic Baló lesions. According to our results, homogeneous and concentric demyelinations may be two different macroscopic outcomes of a single fundamental immune disorder. Furthermore, in chemotactic models, cellular aggressivity appears to play a central role in pattern formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
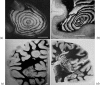
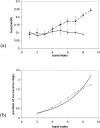

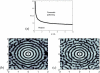
 range of action,
range of action,  . Other parameters are ε = 0,4 and q = 0,1. Interestingly the range of action of the potential φ is larger than in figure 5 whereas the size of the domain is considerably smaller. In fact, this range fully determines the width of the bands. (b) Same illustration with a degenerated potential
. Other parameters are ε = 0,4 and q = 0,1. Interestingly the range of action of the potential φ is larger than in figure 5 whereas the size of the domain is considerably smaller. In fact, this range fully determines the width of the bands. (b) Same illustration with a degenerated potential  . Destroyed oligodendrocytes are figured in black. The size of the domain is four times smaller than in figure 4 (axis labels in cms), whereas the action range is similar.
. Destroyed oligodendrocytes are figured in black. The size of the domain is four times smaller than in figure 4 (axis labels in cms), whereas the action range is similar.
Similar articles
-
Baló's concentric sclerosis: surviving normal myelin in a patient with a relapsing-remitting dinical course.Mult Scler. 2001 Dec;7(6):375-82. doi: 10.1177/135245850100700606. Mult Scler. 2001. PMID: 11795459
-
[Recent progress in multiple sclerosis research: astrocytopathy in demyelinating diseases].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2010 Nov;50(11):788-93. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.50.788. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2010. PMID: 21921443 Review. Japanese.
-
[Balò's concentric sclerosis in a North-African patient].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2005 Jan;161(1):78-80. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(05)84977-x. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2005. PMID: 15678005 French.
-
Exploring the overlap between multiple sclerosis, tumefactive demyelination and Baló's concentric sclerosis.Mult Scler. 2016 Jul;22(8):986-92. doi: 10.1177/1352458516641776. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 27037180 Review.
-
Concentric demyelination by self-organization: a new hypothesis for Baló's sclerosis.Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007 Sep;3(9):E1. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0619. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17805242 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mathematical description of bacterial traveling pulses.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Aug 19;6(8):e1000890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000890. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20808878 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-like tissue injury and glial response contribute to Balo concentric lesion development.Neurology. 2016 Nov 8;87(19):2000-2005. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003308. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27733565 Free PMC article.
-
Basic and advanced imaging of a case of Balò's concentric sclerosis.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Jan 25;2013:bcr2012008413. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008413. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23355596 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
7 Tesla MRI of Balo's concentric sclerosis versus multiple sclerosis lesions.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Jun 29;5(8):900-912. doi: 10.1002/acn3.572. eCollection 2018 Aug. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30128315 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of a Balo's Concentric Sclerosis-Like Lesion in a Young Adult Woman.Cureus. 2023 Oct 10;15(10):e46803. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46803. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37954773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baló J. Leucoencephalitis periaxialis concentrica. Magy Orvosi Arch. 1927;28:108–124.
-
- Hallervorden J, Spatz H. Über die konzentrische Sklerose und die physicalisch-chemischen Faktoren bei der Ausbreitung von Entmarkungsprozessen. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr. 1933;98:641–701.
-
- Lumsden CE. The neuropathology of multiple sclerosis. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW, editors. Handbook of clinical neurology, Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Co.; 1970. pp. 217–319. vol. 9.
-
- Stadelmann C, Brück W. Lessons from the neuropathology of atypical forms of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci. 2004;25:S319–S322. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Chu NS, Lu CS, Sung CY. Serial magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Baló's concentric sclerosis: natural history of lesion development. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:651–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

