Nicotine-induced proliferation of isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells: effect on cell signalling and function
- PMID: 17227300
- PMCID: PMC6496628
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2007.00418.x
Nicotine-induced proliferation of isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells: effect on cell signalling and function
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the current study was to investigate whether nicotine treatment would induce the proliferation of isolated rat primary pancreatic acinar cells in culture by activating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling and exocrine secretion.
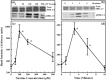
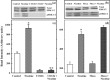
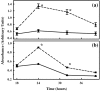
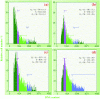
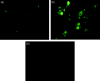
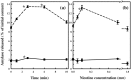
Materials and methods: A nicotine dose- and time-response curve was initially developed to determine the optimal dose and time used for all subsequent studies. Proliferation studies were conducted by cell counting and confirmed further by bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation and flow cytometry assays. MAPK signalling studies were conducted by Western blot analysis. Localization of ERK1/2 signals, with or without nicotine and the MAPK inhibitor, was visualized by immunofluorescence.
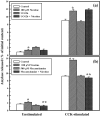
Results: Nicotine treatment caused dose-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), the maxima occurring at 100 micro m and at 3 min after treatment; the response was suppressed by the ERK1/2 inhibitor. Maximal nicotine-induced cell proliferation occurred at 24 h, and UO126-treatment significantly reduced this response. Exposure of cells to 100 microm nicotine for 6 min significantly enhanced both baseline and cholecystokinin-stimulated cell function, and these effects were not affected by treatment with the inhibitor of ERK1/2 but were suppressed by mecamylamine, a nicotinic receptor antagonist.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that nicotine treatment induced cell proliferation of isolated pancreatic acinar cells and that this is coupled with the activation of MAPK signalling with no effect on its function. Hence, in primary cells, the mechanism of induction and regulation of these two processes, cell proliferation and cell function, by nicotine treatment are independent of each other.
Figures
References
-
- Bose C, Zhang H, Udupa KB, Chowdhury P (2005) Activation of p‐ERK1/2 by nicotine in pancreatic tumor cell line AR42J: effects on proliferation and secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 289, G926–G934. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein‐dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo MG, Codignola A, Vicentini LM, Clementi F, Sher E (1993) Nicotine stimulates a serotonergic autocrine loop in human small lung cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 53, 5566–5568. - PubMed
-
- Charland S, Boucher M‐J, Houde M, Rivard N (2001) Somatostatin inhibits Akt phosphorylation and cell cycle entry, but not p42/p44 mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase activation in normal and tumoral pancreatic acinar cells. Endocrinology 142, 121–128. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury P, Rayford PL (2000) Smoking and pancreatic disorders. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 869–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

