Differential roles of Rap1 and Rap2 small GTPases in neurite retraction and synapse elimination in hippocampal spiny neurons
- PMID: 17227435
- PMCID: PMC12125706
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04195.x
Differential roles of Rap1 and Rap2 small GTPases in neurite retraction and synapse elimination in hippocampal spiny neurons
Abstract
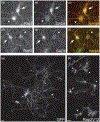
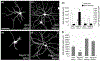
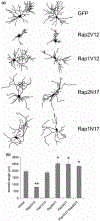
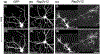
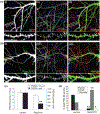
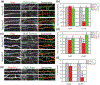
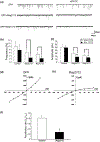
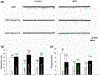
The Rap family of small GTPases is implicated in the mechanisms of synaptic plasticity, particularly synaptic depression. Here we studied the role of Rap in neuronal morphogenesis and synaptic transmission in cultured neurons. Constitutively active Rap2 expressed in hippocampal pyramidal neurons caused decreased length and complexity of both axonal and dendritic branches. In addition, Rap2 caused loss of dendritic spines and spiny synapses, and an increase in filopodia-like protrusions and shaft synapses. These Rap2 morphological effects were absent in aspiny interneurons. In contrast, constitutively active Rap1 had no significant effect on axon or dendrite morphology. Dominant-negative Rap mutants increased dendrite length, indicating that endogenous Rap restrains dendritic outgrowth. The amplitude and frequency of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA)-mediated miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) decreased in hippocampal neurons transfected with active Rap1 or Rap2, associated with reduced surface and total levels of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2. Finally, increasing synaptic activity with GABA(A) receptor antagonists counteracted Rap2's inhibitory effect on dendrite growth, and masked the effects of Rap1 and Rap2 on AMPA-mediated mEPSCs. Rap1 and Rap2 thus have overlapping but distinct actions that potentially link the inhibition of synaptic transmission with the retraction of axons and dendrites.
Figures
References
-
- Bito H, Furuyashiki T, Ishihara H, Shibasaki Y, Ohashi K, Mizuno K, Maekawa M, Ishizaki T and Narumiya S (2000) A critical role for a Rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK, in determining axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron 26, 431–441. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL (1997) Ras-like GTPases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1333, M19–M31. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Wang PY and Ghosh A (2005) Regulation of cortical dendrite development by Rap1 signaling. Mol. Cell. Neurosci 28, 215–228. - PubMed
-
- Coleman PD and Yao PJ (2003) Synaptic slaughter in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 24, 1023–1027. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

