Mechanism of thioamide drug action against tuberculosis and leprosy
- PMID: 17227913
- PMCID: PMC2118422
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062100
Mechanism of thioamide drug action against tuberculosis and leprosy
Abstract
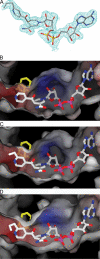
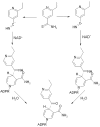
Thioamide drugs, ethionamide (ETH) and prothionamide (PTH), are clinically effective in the treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. leprae, and M. avium complex infections. Although generally considered second-line drugs for tuberculosis, their use has increased considerably as the number of multidrug resistant and extensively drug resistant tuberculosis cases continues to rise. Despite the widespread use of thioamide drugs to treat tuberculosis and leprosy, their precise mechanisms of action remain unknown. Using a cell-based activation method, we now have definitive evidence that both thioamides form covalent adducts with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and that these adducts are tight-binding inhibitors of M. tuberculosis and M. leprae InhA. The crystal structures of the inhibited M. leprae and M. tuberculosis InhA complexes provide the molecular details of target-drug interactions. The purified ETH-NAD and PTH-NAD adducts both showed nanomolar Kis against M. tuberculosis and M. leprae InhA. Knowledge of the precise structures and mechanisms of action of these drugs provides insights into designing new drugs that can overcome drug resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Fajardo, T.T., R.S. Guinto, R.V. Cellona, R.M. Abalos, E.C. Dela Cruz, and R.H. Gelber. 2006. A clinical trial of ethionamide and prothionamide for treatment of lepromatous leprosy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 74:457–461. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2006. Emergence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with extensive resistance to second-line drugs–worldwide, 2000-2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 55:301–305. - PubMed
-
- Crofton, J., P. Chaulet, D. Maher, J. Grosset, W. Harris, H. Norman, M. Iseman, and B. Watt. 1997. Guidelines for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Katoch, K., M. Natarajan, A.S. Bhatia, and V.S. Yadav. 1992. Treatment of paucibacillary leprosy with a regimen containing rifampicin, dapsone and prothionamide. Indian J. Lepr. 64:303–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

