Acid pH activation of the PmrA/PmrB two-component regulatory system of Salmonella enterica
- PMID: 17229213
- PMCID: PMC1804205
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05512.x
Acid pH activation of the PmrA/PmrB two-component regulatory system of Salmonella enterica
Abstract
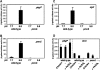
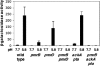
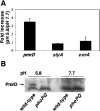
Acid pH often triggers changes in gene expression. However, little is known about the identity of the gene products that sense fluctuations in extracytoplasmic pH. The Gram-negative pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium experiences a number of acidic environments both inside and outside animal hosts. Growth in mild acid (pH 5.8) promotes transcription of genes activated by the response regulator PmrA, but the signalling pathway(s) that mediates this response has thus far remained unexplored. Here we report that this activation requires both PmrA's cognate sensor kinase PmrB, which had been previously shown to respond to Fe(3+) and Al(3+), and PmrA's post-translational activator PmrD. Substitution of a conserved histidine or of either one of four conserved glutamic acid residues in the periplasmic domain of PmrB severely decreased or abolished the mild acid-promoted transcription of PmrA-activated genes. The PmrA/PmrB system controls lipopolysaccharide modifications mediating resistance to the antibiotic polymyxin B. Wild-type Salmonella grown at pH 5.8 were > 100 000-fold more resistant to polymyxin B than organisms grown at pH 7.7. Our results suggest that protonation of the PmrB periplasmic histidine and/or of the glutamic acid residues activate the PmrA protein, and that mild acid promotes cellular changes resulting in polymyxin B resistance.
Figures
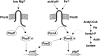


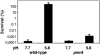
References
-
- Breazeale SD, Ribeiro AA, Raetz CRH. Origin of lipid A species modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose in polymyxin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli: an aminotransferase (ArnB) that generates UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:24731–24739. - PubMed
-
- Brumell JH, Grinstein S. Salmonella redirects phagosomal maturation. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004;7:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Chamnongpol S, Dodson W, Cromie MJ, Harris ZL, Groisman EA. Fe(III)-mediated cellular toxicity. Mol Microbiol. 2002;45:711–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

