Maintenance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells through the association of a viral glycoprotein with PERK, a cellular ER stress sensor
- PMID: 17229688
- PMCID: PMC1866074
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02191-06
Maintenance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells through the association of a viral glycoprotein with PERK, a cellular ER stress sensor
Abstract
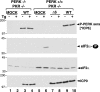
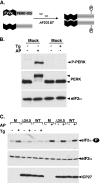
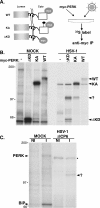
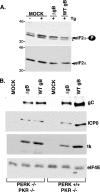
In the efforts of viruses to dominate and control critical cellular pathways, viruses generate considerable intracellular stress within their hosts. In particular, the capacity of resident endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperones to properly process the acute increase in client protein load is significantly challenged. Such alterations typically induce the unfolded protein response, one component of which acts through IRE1 to restore ER homeostasis by expanding the folding capabilities, whereas the other arm activates the eIF-2alpha (alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2) kinase PERK to transiently arrest production of new polypeptide clientele. Viruses, such as herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), however, go to great lengths to prevent the inhibition of translation resulting from eIF-2alpha phosphorylation. Here, we establish that PERK, but not IRE1, resists activation by acute ER stress in HSV-1-infected cells. This requires the ER luminal domain of PERK, which associates with the viral glycoprotein gB. Strikingly, gB regulates viral protein accumulation in a PERK-dependent manner. This is the first description of a virus-encoded PERK-specific effector and defines a new strategy by which viruses are able to maintain ER homeostasis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 infection activates the endoplasmic reticulum resident kinase PERK and mediates eIF-2alpha dephosphorylation by the gamma(1)34.5 protein.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1379-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1379-1388.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650164 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of mRNA translation to acute endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing agents in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells requires multiple virus-encoded functions.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7354-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00479-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840316 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 UL34 Protein Regulates the Global Architecture of the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Infected Cells.J Virol. 2017 May 26;91(12):e00271-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00271-17. Print 2017 Jun 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28356536 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of stress, Ca2+, and immunogenic signaling pathways by PERK at the endoplasmic reticulum.Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 1;397(7):649-56. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2016-0108. Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26872313 Review.
-
The PERKs of mitochondria protection during stress: insights for PERK modulation in neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Oct;97(5):1737-1748. doi: 10.1111/brv.12860. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 35475315 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic herpes simplex virus counteracts the hypoxia-induced modulation of glioblastoma stem-like cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012 Apr;1(4):322-32. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2011-0035. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23197811 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus 2 infection impacts stress granule accumulation.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):8119-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00313-12. Epub 2012 May 23. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22623775 Free PMC article.
-
The Unfolded Protein Response: Detecting and Responding to Fluctuations in the Protein-Folding Capacity of the Endoplasmic Reticulum.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Sep 3;11(9):a033886. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033886. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30670466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unfolded protein response and autophagy: herpesviruses rule!J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(3):1168-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01358-08. Epub 2008 Sep 10. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18787009 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Restriction of Replication of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus with a Deletion of γ34.5 in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00246-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00246-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29793956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertolotti, A., Y. Zhang, L. M. Hendershot, H. P. Harding, and D. Ron. 2000. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:326-332. - PubMed
-
- Besemer, J., H. Harant, S. Wang, B. Oberhauser, K. Marquardt, C. A. Foster, E. P. Schreiner, J. E. de Vries, C. Dascher-Nadel, and I. J. Lindley. 2005. Selective inhibition of cotranslational translocation of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Nature 436:290-293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

