Targeting of the Sendai virus C protein to the plasma membrane via a peptide-only membrane anchor
- PMID: 17229713
- PMCID: PMC1866060
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02465-06
Targeting of the Sendai virus C protein to the plasma membrane via a peptide-only membrane anchor
Abstract
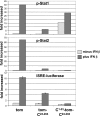
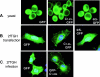
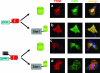
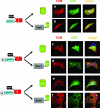
Several cellular proteins are synthesized in the cytosol on free ribosomes and then associate with membranes due to the presence of short peptide sequences. These membrane-targeting sequences contain sites to which lipid chains are attached, which help direct the protein to a particular membrane domain and anchor it firmly in the bilayer. The intracellular concentration of these proteins in particular cellular compartments, where their interacting partners are also concentrated, is essential to their function. This paper reports that the apparently unmodified N-terminal sequence of the Sendai virus C protein (MPSFLKKILKLRGRR . . .; letters in italics represent hydrophobic residues; underlined letters represent basic residues, which has a strong propensity to form an amphipathic alpha-helix in a hydrophobic environment) also function as a membrane targeting signal and membrane anchor. Moreover, the intracellular localization of the C protein at the plasma membrane is essential for inducing the interferon-independent phosphorylation of Stat1 as part of the viral program to prevent the cellular antiviral response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A short peptide at the amino terminus of the Sendai virus C protein acts as an independent element that induces STAT1 instability.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(16):8799-811. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8799-8811.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15280488 Free PMC article.
-
NMR structure and molecular dynamics of the in-plane membrane anchor of nonstructural protein 5A from bovine viral diarrhea virus.Biochemistry. 2006 Feb 21;45(7):2221-33. doi: 10.1021/bi0517685. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16475810
-
A complex peptide-sorting signal, but no mRNA signal, is required for the Sec-independent transport of Ist2 from the yeast ER to the plasma membrane.FEBS Lett. 2007 Feb 6;581(3):401-5. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.12.048. Epub 2007 Jan 10. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17234190
-
Interactions of Ras proteins with the plasma membrane and their roles in signaling.Cell Signal. 2008 Jan;20(1):31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.07.012. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 17888630 Review.
-
Membrane binding of lipidated Ras peptides and proteins--the structural point of view.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1788(1):273-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.006. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18771652 Review.
Cited by
-
Degradation, Promoter Recruitment and Transactivation Mediated by the Extreme N-Terminus of MHC Class II Transactivator CIITA Isoform III.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0148753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148753. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26871568 Free PMC article.
-
Two domains of the V protein of virulent canine distemper virus selectively inhibit STAT1 and STAT2 nuclear import.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(13):6328-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01878-09. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20427537 Free PMC article.
-
Clustered basic amino acids of the small sendai virus C protein Y1 are critical to its RAN GTPase-mediated nuclear localization.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 9;8(8):e73740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073740. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951363 Free PMC article.
-
The C proteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 block IFN signaling by binding and retaining Stat1 in perinuclear aggregates at the late endosome.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e28382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028382. Epub 2012 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22355301 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the beta interferon promoter by unnatural Sendai virus infection requires RIG-I and is inhibited by viral C proteins.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(22):12227-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01300-07. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17804509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrami, L., M. Fivaz, and F. G. van der Goot. 2000. Surface dynamics of aerolysin on the plasma membrane of living cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 290:363-367. - PubMed
-
- Ali, B. R., C. Wasmeier, L. Lamoreux, M. Strom, and M. C. Seabra. 2004. Multiple regions contribute to membrane targeting of Rab GTPases. J. Cell Sci. 117:6401-6412. - PubMed
-
- Arbuzova, A., L. Wang, J. Wang, G. Hangyas-Mihalyne, D. Murray, B. Honig, and S. McLaughlin. 2000. Membrane binding of peptides containing both basic and aromatic residues. Experimental studies with peptides corresponding to the scaffolding region of caveolin and the effector region of MARCKS. Biochemistry 39:10330-10339. - PubMed
-
- Bates, I. R., J. B. Feix, J. M. Boggs, and G. Harauz. 2004. An immunodominant epitope of myelin basic protein is an amphipathic alpha-helix. J. Biol. Chem. 279:5757-5764. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

