Convergent extension, planar-cell-polarity signalling and initiation of mouse neural tube closure
- PMID: 17229766
- PMCID: PMC1839770
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.000380
Convergent extension, planar-cell-polarity signalling and initiation of mouse neural tube closure
Abstract
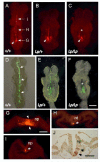
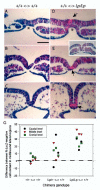
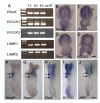
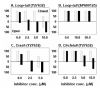
Planar-cell-polarity (PCP) signalling is necessary for initiation of neural tube closure in higher vertebrates. In mice with PCP gene mutations, a broad embryonic midline prevents the onset of neurulation through wide spacing of the neural folds. In order to evaluate the role of convergent extension in this defect, we vitally labelled the midline of loop-tail (Lp) embryos mutant for the PCP gene Vangl2. Injection of DiI into the node, and electroporation of a GFP expression vector into the midline neural plate, revealed defective convergent extension in both axial mesoderm and neuroepithelium, before the onset of neurulation. Chimeras containing both wild-type and Lp-mutant cells exhibited mainly wild-type cells in the midline neural plate and notochordal plate, consistent with a cell-autonomous disturbance of convergent extension. Inhibitor studies in whole-embryo culture demonstrated a requirement for signalling via RhoA-Rho kinase, but not jun N-terminal kinase, in convergent extension and the onset of neural tube closure. These findings identify a cell-autonomous defect of convergent extension, requiring PCP signalling via RhoA-Rho kinase, during the development of severe neural tube defects in the mouse.
Figures




References
-
- Ang S-L, Rossant J. HNF-3β is essential for node and notochord formation in mouse development. Cell. 1994;78:561–574. - PubMed
-
- Bastock R, Strutt H, Strutt D. Strabismus is asymmetrically localised and binds to Prickle and Dishevelled during Drosophila planar polarity patterning. Development. 2003;130:3007–3014. - PubMed
-
- Beddington RS, Robertson EJ. An assessment of the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells in the midgestation mouse embryo. Development. 1989;105:733–737. - PubMed
-
- Beddington RSP. Induction of a second neural axis by the mouse node. Development. 1994;120:613–620. - PubMed
-
- Botto LD, Moore CA, Khoury MJ, Erickson JD. Neural-tube defects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;341:1509–1519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

