Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor
- PMID: 17229951
- PMCID: PMC2670197
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa063988
Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor
Abstract
Background: A single family has been described in which obesity results from a mutation in the leptin-receptor gene (LEPR), but the prevalence of such mutations in severe, early-onset obesity has not been systematically examined.
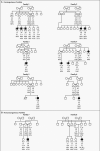
Methods: We sequenced LEPR in 300 subjects with hyperphagia and severe early-onset obesity, including 90 probands from consanguineous families, and investigated the extent to which mutations cosegregated with obesity and affected receptor function. We evaluated metabolic, endocrine, and immune function in probands and affected relatives.
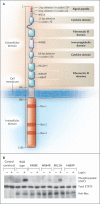
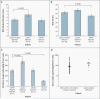
Results: Of the 300 subjects, 8 (3%) had nonsense or missense LEPR mutations--7 were homozygotes, and 1 was a compound heterozygote. All missense mutations resulted in impaired receptor signaling. Affected subjects were characterized by hyperphagia, severe obesity, alterations in immune function, and delayed puberty due to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Serum leptin levels were within the range predicted by the elevated fat mass in these subjects. Their clinical features were less severe than those of subjects with congenital leptin deficiency.
Conclusions: The prevalence of pathogenic LEPR mutations in a cohort of subjects with severe, early-onset obesity was 3%. Circulating levels of leptin were not disproportionately elevated, suggesting that serum leptin cannot be used as a marker for leptin-receptor deficiency. Congenital leptin-receptor deficiency should be considered in the differential diagnosis in any child with hyperphagia and severe obesity in the absence of developmental delay or dysmorphism.
Copyright 2007 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Kiess W, Galler A, Reich A, et al. Clinical aspects of obesity in childhood and adolescence. Obes Rev. 2001;2:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. Monogenic obesity in humans. Annu Rev Med. 2005;56:443–58. - PubMed
-
- Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, et al. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature. 1997;387:903–8. - PubMed
-
- Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD. A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nat Genet. 1998;18:213–5. - PubMed
-
- Clement K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, et al. A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature. 1998;392:398–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
