Efficient immortalization of primary human cells by p16INK4a-specific short hairpin RNA or Bmi-1, combined with introduction of hTERT
- PMID: 17233832
- PMCID: PMC11158394
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00373.x
Efficient immortalization of primary human cells by p16INK4a-specific short hairpin RNA or Bmi-1, combined with introduction of hTERT
Abstract
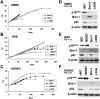
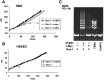
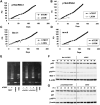
Activation of telomerase is sufficient for immortalization of some types of human cells but additional factors may also be essential. It has been proposed that stress imposed by inadequate culture conditions induces senescence due to accumulation of p16(INK4a). Here, we present evidence that many human cell types undergo senescence by activation of the p16(INK4a)/Rb pathway, and that introduction of Bmi-1 can inhibit p16(INK4a) expression and extend the life span of human epithelial cells derived from skin, mammary gland and lung. Introduction of p16(INK4a)-specific short hairpin RNA, as well as Bmi-1, suppressed p16(INK4a) expression in human mammary epithelial cells without promoter methylation, and extended their life span. Subsequent introduction of hTERT, the telomerase catalytic subunit, into cells with low p16(INK4a) levels resulted in efficient immortalization of three cell types without crisis or growth arrest. The majority of the human mammary epithelial cells thus immortalized showed almost normal ploidy as judged by G-banding and spectral karyotyping analysis. Our data suggest that inhibition of p16(INK4a) and introduction of hTERT can immortalize many human cell types with little chromosomal instability.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Human keratinocytes that express hTERT and also bypass a p16(INK4a)-enforced mechanism that limits life span become immortal yet retain normal growth and differentiation characteristics.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;20(4):1436-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1436-1447.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648628 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic changes in human epithelial cells immortalized by telomerase.Am J Pathol. 2000 May;156(5):1537-47. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65025-0. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10793065 Free PMC article.
-
Bmi-1 reduction plays a key role in physiological and premature aging of primary human keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2010 Apr;130(4):1048-62. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.355. Epub 2009 Nov 12. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 19907431
-
Control of the replicative life span of human fibroblasts by p16 and the polycomb protein Bmi-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(1):389-401. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.389-401.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12482990 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular changes accompanying senescence and immortalization of cultured human mammary epithelial cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;34(11):1382-94. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00047-x. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12200033 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of immortalized primary cell from the critically endangered Bonin flying fox (Pteropus pselaphon).PLoS One. 2019 Aug 26;14(8):e0221364. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221364. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31449544 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of cell lines from adult T-cell leukemia cells dependent on negatively charged polymers.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2017 Jul 5;57(1):9-14. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.16021. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2017. PMID: 28420813 Free PMC article.
-
Novel human bronchial epithelial cell lines for cystic fibrosis research.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jan;296(1):L82-91. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90314.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18978040 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated control of senescence by lncRNA and a novel T-box3 co-repressor complex.Elife. 2014 May 29;3:e02805. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02805. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24876127 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and genetic characterization of cell lines derived from proliferating nasal polyps and sinonasal inverted papillomas.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 24;11(1):17100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96444-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34429452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayflick L, Moohead PS. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 1965; 37: 614 – 36. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J. Cellular senescence as a tumor‐suppressor mechanism. Trends Cell Biol 2001; 11: S27 – 31. - PubMed
-
- Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M et al. Extension of life‐span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 1998; 279: 349 – 52. - PubMed
-
- Kiyono T, Foster SA, Koop JI, McDougall JK, Galloway DA, Klingelhutz AJ. Both Rb/p16INK4a inactivation and telomerase activity are required to immortalize human epithelial cells. Nature 1998; 396: 84 – 8. - PubMed
-
- Jarrard DF, Sarkar S, Shi Y et al. p16/pRb pathway alterations are required for bypassing senescence in human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2957 – 64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

