Inventing an arsenal: adaptive evolution and neofunctionalization of snake venom phospholipase A2 genes
- PMID: 17233905
- PMCID: PMC1783844
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-2
Inventing an arsenal: adaptive evolution and neofunctionalization of snake venom phospholipase A2 genes
Abstract
Background: Gene duplication followed by functional divergence has long been hypothesized to be the main source of molecular novelty. Convincing examples of neofunctionalization, however, remain rare. Snake venom phospholipase A2 genes are members of large multigene families with many diverse functions, thus they are excellent models to study the emergence of novel functions after gene duplications.
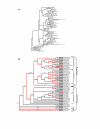
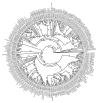
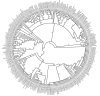
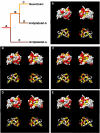
Results: Here, I show that positive Darwinian selection and neofunctionalization is common in snake venom phospholipase A2 genes. The pattern of gene duplication and positive selection indicates that adaptive molecular evolution occurs immediately after duplication events as novel functions emerge and continues as gene families diversify and are refined. Surprisingly, adaptive evolution of group-I phospholipases in elapids is also associated with speciation events, suggesting adaptation of the phospholipase arsenal to novel prey species after niche shifts. Mapping the location of sites under positive selection onto the crystal structure of phospholipase A2 identified regions evolving under diversifying selection are located on the molecular surface and are likely protein-protein interactions sites essential for toxin functions.
Conclusion: These data show that increases in genomic complexity (through gene duplications) can lead to phenotypic complexity (venom composition) and that positive Darwinian selection is a common evolutionary force in snake venoms. Finally, regions identified under selection on the surface of phospholipase A2 enzymes are potential candidate sites for structure based antivenin design.
Figures




References
-
- Dennis EA. Phospholipases. In: Boyer PD, editor. The Enzymes. 3rd. Vol. 16. New York, Academic Press; 1983.
-
- Kini RM. Venom Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Structure, Function and Mechanism. Chichester, Wiley; 1997. p. 511.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

