Novel dexamethasone-HPMA copolymer conjugate and its potential application in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17233911
- PMCID: PMC1860059
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2106
Novel dexamethasone-HPMA copolymer conjugate and its potential application in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
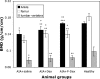
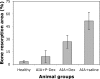
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease of unknown etiology. Effective treatment of this disorder has been hampered by the lack of availability of agents that selectively target affected joint tissue. We developed a novel pH-sensitive drug delivery system of dexamethasone (Dex) based on an N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymer (P-Dex) and have shown that the delivery system specifically accumulates in inflamed joints in an animal model of arthritis. We hypothesize that the arthrotropism of the delivery system and the local acidosis-mediated drug release provide superior therapeutic efficacy and potentially reduced side effects in RA treatment. The initial in vitro drug-release study confirmed that the Dex release is indeed dependent upon the environmental pH. At pH 5, 37 degrees C, the conjugate shows the highest level of drug release. When administered systemically in an adjuvant-induced arthritis rat model, P-Dex offers superior and longer-lasting anti-inflammatory effects compared with systemically administered free Dex. In addition, greater bone and cartilage preservation was observed with the P-Dex treatment compared with free Dex treatment. Our data indicate that the differential effect of the conjugate is related to its selective accumulation, potential macrophage-mediated retention, and pH-sensitive drug release (extracellular and intracellular) in arthritic joints. This newly developed drug delivery system provides a unique method for selective targeting of glucocorticoids to inflamed joints which may potentially reduce systemic side effects.
Figures
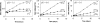
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and evaluation of a well-defined HPMA copolymer-dexamethasone conjugate for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Pharm Res. 2008 Dec;25(12):2910-9. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9683-3. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 18649124 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a macromolecular prodrug for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis: mechanisms involved in arthrotropism and sustained therapeutic efficacy.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R170. doi: 10.1186/ar3130. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20836843 Free PMC article.
-
The Evaluation of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Side Effects of a Macromolecular Dexamethasone Prodrug in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model.Pharm Res. 2016 Jan;33(1):186-93. doi: 10.1007/s11095-015-1776-1. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 26286188 Free PMC article.
-
Improving dexamethasone drug loading and efficacy in treating rheumatoid arthritis via liposome: Focusing on inflammation and molecular mechanisms.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 Jan;8(1):5-19. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12518. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39627850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric delivery systems for dexamethasone.Life Sci. 2014 Feb 6;96(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.12.020. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24373835 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone Conjugates: Synthetic Approaches and Medical Prospects.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 27;9(4):341. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040341. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33801776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-articular targeting of nanomaterials for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jul 15;93:239-257. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.010. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30862551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-related histopathology and bone remodeling characteristics of the knee articular cartilage and subchondral bone induced by glucocorticoids in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jun;17(6):4492-4498. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7508. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31105787 Free PMC article.
-
HPMA-Copolymer Nanocarrier Targets Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Dec;16(12):2701-2710. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0995. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28830983 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarriers for vascular delivery of anti-inflammatory agents.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;54:205-26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011613-140002. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24392694 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Harris ED Jr., Budd RC, Genovese MC, Firestein GS, Sargent JS, Sledge CB, editor. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 7. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2005. pp. 996–1042.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

