Goal-related activity in hippocampal place cells
- PMID: 17234580
- PMCID: PMC6672791
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2864-06.2007
Goal-related activity in hippocampal place cells
Abstract
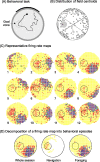
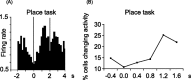
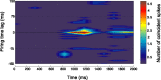
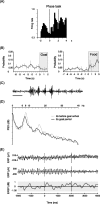
Place cells are hippocampal neurons whose discharge is strongly related to a rat's location in its environment. The existence of place cells has led to the proposal that they are part of an integrated neural system dedicated to spatial navigation, an idea supported by the discovery of strong relationships between place cell activity and spatial problem solving. To further understand such relationships, we examined the discharge of place cells recorded while rats solved a place navigation task. We report that, in addition to having widely distributed firing fields, place cells also discharge selectively while the hungry rat waits in an unmarked goal location to release a food pellet. Such firing is not duplicated in other locations outside the main firing field even when the rat's behavior is constrained to be extremely similar to the behavior at the goal. We therefore propose that place cells provide both a geometric representation of the current environment and a reflection of the rat's expectancy that it is located correctly at the goal. This on-line feedback about a critical aspect of navigational performance is proposed to be signaled by the synchronous activity of the large fraction of place cells active at the goal. In combination with other (prefrontal) cells that provide coarse encoding of goal location, hippocampal place cells may therefore participate in a neural network allowing the rat to plan accurate trajectories in space.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
