Critical role of PA28gamma in hepatitis C virus-associated steatogenesis and hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 17234812
- PMCID: PMC1776165
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607312104
Critical role of PA28gamma in hepatitis C virus-associated steatogenesis and hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
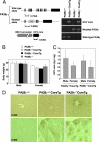
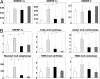
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major cause of chronic liver disease that frequently leads to steatosis, cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCV core protein is not only a component of viral particles but also a multifunctional protein because liver steatosis and HCC are developed in HCV core gene-transgenic (CoreTg) mice. Proteasome activator PA28gamma/REGgamma regulates host and viral proteins such as nuclear hormone receptors and HCV core protein. Here we show that a knockout of the PA28gamma gene induces the accumulation of HCV core protein in the nucleus of hepatocytes of CoreTg mice and disrupts development of both hepatic steatosis and HCC. Furthermore, the genes related to fatty acid biosynthesis and srebp-1c promoter activity were up-regulated by HCV core protein in the cell line and the mouse liver in a PA28gamma-dependent manner. Heterodimer composed of liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha) and retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRalpha) is known to up-regulate srebp-1c promoter activity. Our data also show that HCV core protein enhances the binding of LXRalpha/RXRalpha to LXR-response element in the presence but not the absence of PA28gamma. These findings suggest that PA28gamma plays a crucial role in the development of liver pathology induced by HCV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

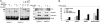

References
-
- Wasley A, Alter MJ. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Bach N, Thung SN, Schaffner F. Hepatology. 1992;15:572–577. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitch JH, Schiff ER, Davis GL, Perrillo RP, Lindsay K, Bodenheimer HC, Jr, Balart LA, Ortego TJ, Payne J, Dienstag JL, et al. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:595–603. - PubMed
-
- Hope RG, McLauchlan J. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:1913–1925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

