The SM protein VPS-45 is required for RAB-5-dependent endocytic transport in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17235359
- PMCID: PMC1796764
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400882
The SM protein VPS-45 is required for RAB-5-dependent endocytic transport in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
Rab5, a small guanosine triphosphatase, is known to regulate the tethering and docking reaction leading to SNARE (soluble NSF attachment protein receptors)-mediated fusion between endosomes. However, it is uncertain how the signal of the activated Rab5 protein is transduced by its downstream effectors during endosome fusion. Here, we show that the Sec1/Munc18 gene vps-45 is essential for not only viability and development but also receptor-mediated and fluid-phase endocytosis pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. We found that VPS-45 interacts with a Rab5 effector, Rabenosyn-5 (RABS-5), and the mutants of both vps-45 and rabs-5 show similar endocytic phenotypes. In the macrophage-like cells of vps-45 and rabs-5 mutants, aberrantly small endosomes were accumulated, and the endosome fusion stimulated by the mutant RAB-5 (Q78L) is suppressed by these mutations. Our results indicate that VPS-45 is a key molecule that functions downstream from RAB-5, cooperating with RABS-5, to regulate the dynamics of the endocytic system in multicellular organisms.
Figures
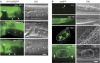
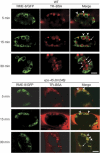
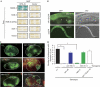
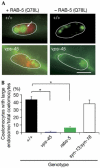
References
-
- Bock JB, Matern HT, Peden AA, Scheller RH (2001) A genomic perspective on membrane compartment organization. Nature 409: 839–841 - PubMed
-
- Bryant NJ, Piper RC, Gerrard SR, Stevens TH (1998) Traffic into the prevacuolar/endosomal compartment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a VPS45-dependent intracellular route and a VPS45-independent, endocytic route. Eur J Cell Biol 76: 43–52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

