Mutations in CUL4B, which encodes a ubiquitin E3 ligase subunit, cause an X-linked mental retardation syndrome associated with aggressive outbursts, seizures, relative macrocephaly, central obesity, hypogonadism, pes cavus, and tremor
- PMID: 17236139
- PMCID: PMC1785336
- DOI: 10.1086/511134
Mutations in CUL4B, which encodes a ubiquitin E3 ligase subunit, cause an X-linked mental retardation syndrome associated with aggressive outbursts, seizures, relative macrocephaly, central obesity, hypogonadism, pes cavus, and tremor
Abstract
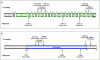
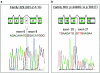
We have identified three truncating, two splice-site, and three missense variants at conserved amino acids in the CUL4B gene on Xq24 in 8 of 250 families with X-linked mental retardation (XLMR). During affected subjects' adolescence, a syndrome emerged with delayed puberty, hypogonadism, relative macrocephaly, moderate short stature, central obesity, unprovoked aggressive outbursts, fine intention tremor, pes cavus, and abnormalities of the toes. This syndrome was first described by Cazebas et al., in a family that was included in our study and that carried a CUL4B missense variant. CUL4B is a ubiquitin E3 ligase subunit implicated in the regulation of several biological processes, and CUL4B is the first XLMR gene that encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase. The relatively high frequency of CUL4B mutations in this series indicates that it is one of the most commonly mutated genes underlying XLMR and suggests that its introduction into clinical diagnostics should be a high priority.
Figures

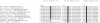

References
Web Resources
-
- BDGP: Splice Site Prediction by Neural Network, http://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/splice.html (for NNSPLICE)
-
- Ensembl Human Genome, http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/index.html
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for CUL4B gene [accession number NM_003588] and protein [accession number NP_003579])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for FMR1, ARX, CUL4B, Angelman syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Börjeson-Forssman-Lehman syndrome, Wilson-Turner syndrome, Parkinson disease, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1, and von Hippel-Lindau disease)
-
- Vega Genome Browser, http://vega.sanger.ac.uk/
References
-
- Poirier K, Lacombe D, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Raynaud M, Desportes V, de Brouwer AP, Moraine C, Fryns JP, Ropers HH, Beldjord C, et al (2006) Screening of ARX in mental retardation families: consequences for the strategy of molecular diagnosis. Neurogenetics 7:39–4610.1007/s10048-005-0014-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

