Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNFalpha in cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening
- PMID: 17236833
- PMCID: PMC1930165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.12.053
Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNFalpha in cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening
Abstract
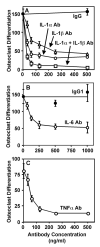
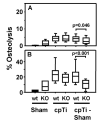
Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF, are considered to be major mediators of osteolysis and ultimately aseptic loosening. This study demonstrated that synergistic interactions among these cytokines are required for the in vitro stimulation of osteoclast differentiation by titanium particles. In contrast, genetic knock out of these cytokines or their receptors does not protect murine calvaria from osteolysis induced by titanium particles. Thus, the extent of osteolysis was not substantially altered in single knock out mice lacking either the IL-1 receptor or IL-6. Osteolysis also was not substantially altered in double knock out mice lacking both the IL-1 receptor and IL-6 or in double knock out mice lacking both TNF receptor-1 and TNF receptor-2. The differences between the in vivo and the cell culture results make it difficult to conclude whether the pro-inflammatory cytokines contribute to aseptic loosening. One alternative is that in vivo experiments are more physiological and that therefore the current results do not support a role for the pro-inflammatory cytokines in aseptic loosening. We however favor the alternative that, in this case, the cell culture experiments can be more informative. We favor this alternative because the role of the pro-inflammatory cytokines may be obscured in vivo by compensation by other cytokines or by the low signal to noise ratio found in measurements of particle-induced osteolysis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Reduction of particle-induced osteolysis by interleukin-6 involves anti-inflammatory effect and inhibition of early osteoclast precursor differentiation.Bone. 2009 Oct;45(4):661-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19524707 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal implant debris-induced osteolysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003 Oct 15;28(20):S125-38. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200310151-00006. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. PMID: 14560184
-
Osteopontin deficiency impairs wear debris-induced osteolysis via regulation of cytokine secretion from murine macrophages.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 May;62(5):1329-37. doi: 10.1002/art.27400. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20155835
-
Particle-Induced Osteolysis Is Mediated by TIRAP/Mal in Vitro and in Vivo: Dependence on Adherent Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016 Feb 17;98(4):285-94. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.O.00736. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016. PMID: 26888676
-
Involvement of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis in the progression of aseptic loosening of total joint arthroplasties: a review of molecular mechanisms.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;395(7):757-767. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02232-4. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35377011 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces inflammatory bone loss in golden Syrian hamsters.Nat Commun. 2022 May 9;13(1):2539. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30195-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35534483 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroethanolic Extract of Polygonum aviculare L. Mediates the Anti-Inflammatory Activity in RAW 264.7 Murine Macrophages Through Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 and Inhibition of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;13(23):3314. doi: 10.3390/plants13233314. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683107 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Metal Ion Release After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Study.Orthop Surg. 2020 Apr;12(2):396-403. doi: 10.1111/os.12591. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Orthop Surg. 2020. PMID: 32023362 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 facilitate corneal lymphangiogenesis in response to herpes simplex virus 1 infection.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14451-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01841-14. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25297992 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukins as Mediators of the Tumor Cell-Bone Cell Crosstalk during the Initiation of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 12;22(6):2898. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062898. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wright TM, Goodman SB, editors. Implant Wear in Total Joint Replacement. Rosemount, Ill: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 2001.
-
- Greenfield EM, Bi Y, Ragab AA, Goldberg VM, Nalepka JL, Seabold JM. Does endotoxin contribute to aseptic loosening of orthopaedic implants? J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;72B:179–85. - PubMed
-
- Greenfield E. Particulate Matter and Host Reactions. In: Wnek G, Bowlin G, editors. Encyclopedia of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering. New York: Taylor Francis; 2006. - DOI
-
- Hicks DG, Judkins AR, Sickel JZ, Rosier RN, Puzas JE, O’Keefe RJ. Granular histiocytosis of pelvic lymph nodes following total hip arthroplasty. The presence of wear debris, cytokine production, and immunologically activated macrophages. J Bone Joint Surg. 1996;78A:482–96. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Konttinen Y, Lassus J, Natah S, Ceponis A, Solovieva S, Aspenberg P, Santavirta S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in loosening of total hip replacement (THR) Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996;14:643–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

