Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNFalpha in cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening
- PMID: 17236833
- PMCID: PMC1930165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.12.053
Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNFalpha in cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening
Abstract
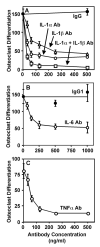
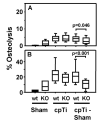
Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF, are considered to be major mediators of osteolysis and ultimately aseptic loosening. This study demonstrated that synergistic interactions among these cytokines are required for the in vitro stimulation of osteoclast differentiation by titanium particles. In contrast, genetic knock out of these cytokines or their receptors does not protect murine calvaria from osteolysis induced by titanium particles. Thus, the extent of osteolysis was not substantially altered in single knock out mice lacking either the IL-1 receptor or IL-6. Osteolysis also was not substantially altered in double knock out mice lacking both the IL-1 receptor and IL-6 or in double knock out mice lacking both TNF receptor-1 and TNF receptor-2. The differences between the in vivo and the cell culture results make it difficult to conclude whether the pro-inflammatory cytokines contribute to aseptic loosening. One alternative is that in vivo experiments are more physiological and that therefore the current results do not support a role for the pro-inflammatory cytokines in aseptic loosening. We however favor the alternative that, in this case, the cell culture experiments can be more informative. We favor this alternative because the role of the pro-inflammatory cytokines may be obscured in vivo by compensation by other cytokines or by the low signal to noise ratio found in measurements of particle-induced osteolysis.
Figures





References
-
- Wright TM, Goodman SB, editors. Implant Wear in Total Joint Replacement. Rosemount, Ill: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 2001.
-
- Greenfield EM, Bi Y, Ragab AA, Goldberg VM, Nalepka JL, Seabold JM. Does endotoxin contribute to aseptic loosening of orthopaedic implants? J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;72B:179–85. - PubMed
-
- Greenfield E. Particulate Matter and Host Reactions. In: Wnek G, Bowlin G, editors. Encyclopedia of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering. New York: Taylor Francis; 2006. - DOI
-
- Hicks DG, Judkins AR, Sickel JZ, Rosier RN, Puzas JE, O’Keefe RJ. Granular histiocytosis of pelvic lymph nodes following total hip arthroplasty. The presence of wear debris, cytokine production, and immunologically activated macrophages. J Bone Joint Surg. 1996;78A:482–96. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Konttinen Y, Lassus J, Natah S, Ceponis A, Solovieva S, Aspenberg P, Santavirta S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in loosening of total hip replacement (THR) Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996;14:643–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

