Positive regulation of fur gene expression via direct interaction of fur in a pathogenic bacterium, Vibrio vulnificus
- PMID: 17237166
- PMCID: PMC1855807
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01791-06
Positive regulation of fur gene expression via direct interaction of fur in a pathogenic bacterium, Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
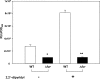
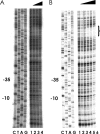
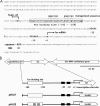
In pathogenic bacteria, the ability to acquire iron, which is mainly regulated by the ferric uptake regulator (Fur), is essential to maintain growth as well as its virulence. In Vibrio vulnificus, a human pathogen causing gastroenteritis and septicemia, fur gene expression is positively regulated by Fur when the iron concentration is limited (H.-J. Lee et al., J. Bacteriol. 185:5891-5896, 2003). Footprinting analysis revealed that an upstream region of the fur gene was protected by the Fur protein from DNase I under iron-depleted conditions. The protected region, from -142 to -106 relative to the transcription start site of the fur gene, contains distinct AT-rich repeats. Mutagenesis of this repeated sequence resulted in abolishment of binding by Fur. To confirm the role of this cis-acting element in Fur-mediated control of its own gene in vivo, fur expression was monitored in V. vulnificus strains using a transcriptional fusion containing the mutagenized Fur-binding site (fur(mt)::luxAB). Expression of fur(mt)::luxAB showed that it was not regulated by Fur and was not influenced by iron concentration. Therefore, this study demonstrates that V. vulnificus Fur acts as a positive regulator under iron-limited conditions by direct interaction with the fur upstream region.
Figures



References
-
- Arluison, V., P. Derreumaux, F. Allemand, M. Folichon, E. Hajnsdorf, and P. Regnier. 2002. Structural modelling of the Sm-like protein Hfq from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 320:705-712. - PubMed
-
- de Fernandez, F. M. T., L. Eoyang, and J. T. August. 1968. Factor fraction required for the synthesis of bacteriophage Qβ-RNA. Nature 219:588-590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

