A novel ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase from the hydrogen-oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacterium Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6
- PMID: 17237175
- PMCID: PMC1855818
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01360-06
A novel ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase from the hydrogen-oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacterium Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6
Abstract
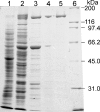
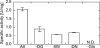
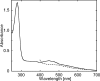
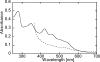
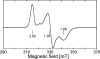
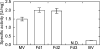
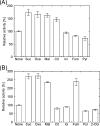
Glutamate synthases are classified according to their specificities for electron donors. Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthases had been found only in plants and cyanobacteria, whereas many bacteria have NADPH-dependent glutamate synthases. In this study, Hydrogenobacter thermophilus, a hydrogen-oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacterium, was shown to possess a ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase like those of phototrophs. This is the first observation, to our knowledge, of a ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase in a nonphotosynthetic organism. The purified enzyme from H. thermophilus was shown to be a monomer of a 168-kDa polypeptide homologous to ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthases from phototrophs. In contrast to known ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthases, the H. thermophilus glutamate synthase exhibited glutaminase activity. Furthermore, this glutamate synthase did not react with a plant-type ferredoxin (Fd3 from this bacterium) containing a [2Fe-2S] cluster but did react with bacterial ferredoxins (Fd1 and Fd2 from this bacterium) containing [4Fe-4S] clusters. Interestingly, the H. thermophilus glutamate synthase was activated by some of the organic acids in the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle, the central carbon metabolic pathway of this organism. This type of activation has not been reported for any other glutamate synthases, and this property may enable the control of nitrogen assimilation by carbon metabolism.
Figures

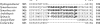
Similar articles
-
Ferredoxin-NADP reductase from the thermophilic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium, Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Aug;297(1):124-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01667.x. Epub 2009 Jun 3. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19552713
-
Enzymatic and electron paramagnetic resonance studies of anabolic pyruvate synthesis by pyruvate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase from Hydrogenobacter thermophilus.FEBS J. 2010 Jan;277(2):501-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07506.x. Epub 2009 Dec 15. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20015072
-
The recombinant alpha subunit of glutamate synthase: spectroscopic and catalytic properties.Biochemistry. 1998 Feb 17;37(7):1828-38. doi: 10.1021/bi972342w. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9485308
-
Structure--function studies on the iron-sulfur flavoenzyme glutamate synthase: an unexpectedly complex self-regulated enzyme.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 1;433(1):193-211. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.033. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581577 Review.
-
Glutamate synthase: structural, mechanistic and regulatory properties, and role in the amino acid metabolism.Photosynth Res. 2005;83(2):191-217. doi: 10.1007/s11120-004-3478-0. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 16143852 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous gene expression and characterization of two serine hydroxymethyltransferases from Thermoplasma acidophilum.Extremophiles. 2021 Jul;25(4):393-402. doi: 10.1007/s00792-021-01238-9. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Extremophiles. 2021. PMID: 34196829
-
PII Protein-Derived FRET Sensors for Quantification and Live-Cell Imaging of 2-Oxoglutarate.Sci Rep. 2017 May 3;7(1):1437. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01440-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28469248 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene retention in plastids of common recent origin.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Jul;27(7):1530-7. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq032. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20123796 Free PMC article.
-
Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase: involvement in ammonium assimilation in Haloferax mediterranei.Extremophiles. 2014 Jan;18(1):147-59. doi: 10.1007/s00792-013-0606-9. Epub 2013 Nov 30. Extremophiles. 2014. PMID: 24292444
-
A soluble NADH-dependent fumarate reductase in the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle of Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6.J Bacteriol. 2008 Nov;190(21):7170-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00747-08. Epub 2008 Aug 29. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18757546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoshima, M., M. Ishii, and Y. Igarashi. 2004. A novel biotin protein required for reductive carboxylation of 2-oxoglutarate by isocitrate dehydrogenase in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6. Mol. Microbiol. 51:791-798. - PubMed
-
- Aoshima, M., M. Ishii, and Y. Igarashi. 2004. A novel enzyme, citryl-CoA synthetase, catalysing the first step of the citrate cleavage reaction in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6. Mol. Microbiol. 52:751-761. - PubMed
-
- Aoshima, M., M. Ishii, and Y. Igarashi. 2004. A novel enzyme, citryl-CoA lyase, catalysing the second step of the citrate cleavage reaction in Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6. Mol. Microbiol. 52:763-770. - PubMed
-
- Bidlingmeyer, B. A., S. A. Cohen, and T. L. Tarvin. 1984. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. 336:93-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

