Pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 17237299
- PMCID: PMC1796695
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39063.689375.55
Pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To quantify the effectiveness of pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance.
Data sources: Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane library searched up to July 2006. Expert opinions sought and reference lists of identified studies and any relevant published reviews checked.
Study selection: Randomised controlled trials that evaluated interventions to delay or prevent type 2 diabetes in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance.
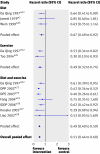
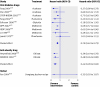
Results: 21 trials met the inclusion criteria, of which 17, with 8084 participants with impaired glucose tolerance, reported results in enough detail for inclusion in the meta-analyses. From the meta-analyses the pooled hazard ratios were 0.51 (95% confidence interval 0.44 to 0.60) for lifestyle interventions v standard advice, 0.70 (0.62 to 0.79) for oral diabetes drugs v control, 0.44 (0.28 to 0.69) for orlistat v control, and 0.32 (0.03 to 3.07) for the herbal remedy jiangtang bushen recipe v standard diabetes advice. These correspond to numbers needed to treat for benefit (NNTB) and harm (NNTH) of 6.4 for lifestyle (95% credible interval, NNTB 5.0 to NNTB 8.4), 10.8 for oral diabetes drugs (NNTB 8.1 to NNTB 15.0), 5.4 for orlistat (NNTB 4.1 to NNTB 7.6), and 4.0 for jiangtang bushen (NNTH 16.9 to NNTB 24.8).
Conclusions: Lifestyle and pharmacological interventions reduce the rate of progression to type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance. Lifestyle interventions seem to be at least as effective as drug treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Review: lifestyle or pharmacological interventions prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance.Evid Based Nurs. 2007 Jul;10(3):78. doi: 10.1136/ebn.10.3.78. Evid Based Nurs. 2007. PMID: 17596383 No abstract available.
-
Review: lifestyle or pharmacologic interventions prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in impaired glucose tolerance.ACP J Club. 2007 Jul-Aug;147(1):1. ACP J Club. 2007. PMID: 17608366 No abstract available.
-
Review: Lifestyle or pharmacological interventions prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in impaired glucose tolerance.Evid Based Med. 2007 Aug;12(4):108. doi: 10.1136/ebm.12.4.108. Evid Based Med. 2007. PMID: 17885156 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davies MJ, Tringham JR, Troughton J, Khunti KK. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. A review of the evidence and its application in a UK setting. Diabet Med 2004;21:403-14. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health. National service framework for diabetes: standards. London: DoH, 2001.
-
- Angelo JB, Huang J, Carden D. Diabetes prevention: a review of current literature. Adv Stud Med 2005;5:250-9.
-
- Anderson DC Jr. Pharmacologic prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Pharmacother 2005;39:102-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous