Regulatory T cell vaccination without autoantigen protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 17237429
- PMCID: PMC9811398
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.3.1791
Regulatory T cell vaccination without autoantigen protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
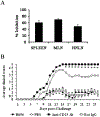
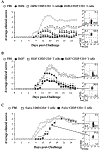
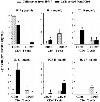
Regulatory T (T(reg)) cells show promise for treating autoimmune diseases, but their induction to elevated potency has been problematic when the most optimally derived cells are from diseased animals. To circumvent reliance on autoantigen-reactive T(reg) cells, stimulation to myelin-independent Ags may offer a viable alternative while maintaining potency to treat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). The experimental Salmonella vaccine expressing colonization factor Ag I possesses anti-inflammatory properties and, when applied therapeutically, reduces further development of EAE in SJL mice. To ascertain T(reg) cell dependency, a kinetic analysis was performed showing increased levels of FoxP3(+)CD25(+)CD4(+) T cells. Inactivation of these T(reg) cells resulted in loss of protection. Adoptive transfer of the vaccine-induced T(reg) cells protected mice against EAE with greater potency than naive or Salmonella vector-induced T(reg) cells, and cytokine analysis revealed enhanced production of TGF-beta, not IL-10. The development of these T(reg) cells in conjunction with immune deviation by Th2 cells optimally induced protective T(reg) cells when compared those induced in the absence of Th2 cells. These data show that T(reg) cells can be induced to high potency to non-disease-inducing Ags using a bacterial vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sospedra M, and Martin R. 2005. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol 23: 683–747. - PubMed
-
- Steinman L 1996. Multiple sclerosis: a coordinated immunological attack against myelin in the central nervous system. Cell 85: 299–302. - PubMed
-
- Zeine R, Heath D, and Owens T. 1993. Enhanced response to antigen within lymph nodes of SJL/J mice that were protected against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by T cell vaccination. J. Neuroimmunol 44: 85–94. - PubMed
-
- Shaw MK, Kim C, Hao HW, Chen F, and Tse HY. 1996. Induction of myelin basic protein-specific experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice: mapping of T cell epitopes and T cell receptor Vβ gene segment usage. J. Neurosci. Res 45: 690–699. - PubMed
-
- Greer JM, Sobel RA, Sette A, Southwood S, Lees MB, and Kuchroo VK. 1996. Immunogenic and encephalitogenic epitope clusters of myelin proteolipid protein. J. Immunol 156: 371–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

