DPL-1 DP, LIN-35 Rb and EFL-1 E2F act with the MCD-1 zinc-finger protein to promote programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17237514
- PMCID: PMC1855110
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.068148
DPL-1 DP, LIN-35 Rb and EFL-1 E2F act with the MCD-1 zinc-finger protein to promote programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
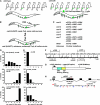
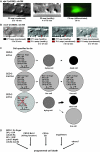
The genes egl-1, ced-9, ced-4, and ced-3 play major roles in programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. To identify genes that have more subtle activities, we sought mutations that confer strong cell-death defects in a genetically sensitized mutant background. Specifically, we screened for mutations that enhance the cell-death defects caused by a partial loss-of-function allele of the ced-3 caspase gene. We identified mutations in two genes not previously known to affect cell death, dpl-1 and mcd-1 (modifier of cell death). dpl-1 encodes the C. elegans homolog of DP, the human E2F-heterodimerization partner. By testing genes known to interact with dpl-1, we identified roles in cell death for four additional genes: efl-1 E2F, lin-35 Rb, lin-37 Mip40, and lin-52 dLin52. mcd-1 encodes a novel protein that contains one zinc finger and that is synthetically required with lin-35 Rb for animal viability. dpl-1 and mcd-1 act with efl-1 E2F and lin-35 Rb to promote programmed cell death and do so by regulating the killing process rather than by affecting the decision between survival and death. We propose that the DPL-1 DP, MCD-1 zinc finger, EFL-1 E2F, LIN-35 Rb, LIN-37 Mip40, and LIN-52 dLin52 proteins act together in transcriptional regulation to promote programmed cell death.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C. elegans orthologs of components of the RB tumor suppressor complex have distinct pro-apoptotic functions.Development. 2007 Oct;134(20):3691-701. doi: 10.1242/dev.004606. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Development. 2007. PMID: 17881492
-
Promotion of oogenesis and embryogenesis in the C. elegans gonad by EFL-1/DPL-1 (E2F) does not require LIN-35 (pRB).Development. 2006 Aug;133(16):3147-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.02490. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Development. 2006. PMID: 16854972
-
dpl-1 DP and efl-1 E2F act with lin-35 Rb to antagonize Ras signaling in C. elegans vulval development.Mol Cell. 2001 Mar;7(3):461-73. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00194-0. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11463372
-
The ins and outs of programmed cell death during C. elegans development.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Aug 30;345(1313):243-6. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0100. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994. PMID: 7846120 Review.
-
The molecular mechanism of programmed cell death in C. elegans.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;887:92-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07925.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10668467 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordinated regulation of intestinal functions in C. elegans by LIN-35/Rb and SLR-2.PLoS Genet. 2008 Apr 25;4(4):e1000059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000059. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18437219 Free PMC article.
-
Horvitz and Sulston on Caenorhabditis elegans Cell Lineage Mutants.Genetics. 2016 Aug;203(4):1485-7. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.193003. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27516609 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
GSK-3 promotes S-phase entry and progression in C. elegans germline stem cells to maintain tissue output.Development. 2018 May 14;145(10):dev161042. doi: 10.1242/dev.161042. Development. 2018. PMID: 29695611 Free PMC article.
-
Wake-up-call, a lin-52 paralogue, and Always early, a lin-9 homologue physically interact, but have opposing functions in regulating testis-specific gene expression.Dev Biol. 2011 Jul 15;355(2):381-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.04.030. Epub 2011 May 4. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21570388 Free PMC article.
-
RB goes mitochondrial.Genes Dev. 2013 May 1;27(9):975-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.219451.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23651852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beitel, G. J., S. G. Clark and H. R. Horvitz, 1990. Caenorhabditis elegans ras gene let-60 acts as a switch in the pathway of vulval induction. Nature 348: 503–509. - PubMed
-
- Bender, A. M., O. Wells and D. S. Fay, 2004. lin-35/Rb and xnp-1/ATR-X function redundantly to control somatic gonad development in C. elegans. Dev. Biol. 273: 335–349. - PubMed
-
- Boxem, M., and S. van den Heuvel, 2001. lin-35 Rb and cki-1 Cip/Kip cooperate in developmental regulation of G1 progression in C. elegans. Development 128: 4349–4359. - PubMed
-
- Boxem, M., and S. van den Heuvel, 2002. C. elegans class B synthetic multivulva genes act in G(1) regulation. Curr. Biol. 12: 906–911. - PubMed
-
- Bracken, A. P., M. Ciro, A. Cocito and K. Helin, 2004. E2F target genes: unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29: 409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

