DPL-1 DP, LIN-35 Rb and EFL-1 E2F act with the MCD-1 zinc-finger protein to promote programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17237514
- PMCID: PMC1855110
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.068148
DPL-1 DP, LIN-35 Rb and EFL-1 E2F act with the MCD-1 zinc-finger protein to promote programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
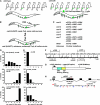
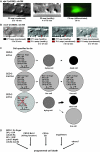
The genes egl-1, ced-9, ced-4, and ced-3 play major roles in programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. To identify genes that have more subtle activities, we sought mutations that confer strong cell-death defects in a genetically sensitized mutant background. Specifically, we screened for mutations that enhance the cell-death defects caused by a partial loss-of-function allele of the ced-3 caspase gene. We identified mutations in two genes not previously known to affect cell death, dpl-1 and mcd-1 (modifier of cell death). dpl-1 encodes the C. elegans homolog of DP, the human E2F-heterodimerization partner. By testing genes known to interact with dpl-1, we identified roles in cell death for four additional genes: efl-1 E2F, lin-35 Rb, lin-37 Mip40, and lin-52 dLin52. mcd-1 encodes a novel protein that contains one zinc finger and that is synthetically required with lin-35 Rb for animal viability. dpl-1 and mcd-1 act with efl-1 E2F and lin-35 Rb to promote programmed cell death and do so by regulating the killing process rather than by affecting the decision between survival and death. We propose that the DPL-1 DP, MCD-1 zinc finger, EFL-1 E2F, LIN-35 Rb, LIN-37 Mip40, and LIN-52 dLin52 proteins act together in transcriptional regulation to promote programmed cell death.
Figures
References
-
- Beitel, G. J., S. G. Clark and H. R. Horvitz, 1990. Caenorhabditis elegans ras gene let-60 acts as a switch in the pathway of vulval induction. Nature 348: 503–509. - PubMed
-
- Bender, A. M., O. Wells and D. S. Fay, 2004. lin-35/Rb and xnp-1/ATR-X function redundantly to control somatic gonad development in C. elegans. Dev. Biol. 273: 335–349. - PubMed
-
- Boxem, M., and S. van den Heuvel, 2001. lin-35 Rb and cki-1 Cip/Kip cooperate in developmental regulation of G1 progression in C. elegans. Development 128: 4349–4359. - PubMed
-
- Boxem, M., and S. van den Heuvel, 2002. C. elegans class B synthetic multivulva genes act in G(1) regulation. Curr. Biol. 12: 906–911. - PubMed
-
- Bracken, A. P., M. Ciro, A. Cocito and K. Helin, 2004. E2F target genes: unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29: 409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

