The role of nonhomologous end-joining components in telomere metabolism in Kluyveromyces lactis
- PMID: 17237517
- PMCID: PMC1840097
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.067447
The role of nonhomologous end-joining components in telomere metabolism in Kluyveromyces lactis
Abstract
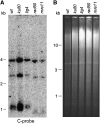
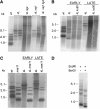
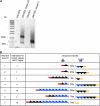
The relationship between telomeres and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) is paradoxical, as NHEJ proteins are part of the telomere cap, which serves to differentiate telomeres from DNA double-strand breaks. We explored these contradictory functions for NHEJ proteins by investigating their role in Kluyveromyces lactis telomere metabolism. The ter1-4LBsr allele of the TER1 gene resulted in the introduction of sequence altered telomeric repeats and subsequent telomere-telomere fusions (T-TFs). In this background, Lig4 and Ku80 were necessary for T-TFs to form. Nej1, essential for NHEJ at internal positions, was not. Hence, T-TF formation was mediated by an unusual NHEJ mechanism. Rad50 and mre11 strains exhibited stable short telomeres, suggesting that Rad50 and Mre11 were required for telomerase recruitment. Introduction of the ter1-4LBsr allele into these strains failed to result in telomere elongation as normally observed with the ter1-4LBsr allele. Thus, the role of Rad50 and Mre11 in the formation of T-TFs was unclear. Furthermore, rad50 and mre11 mutants had highly increased subtelomeric recombination rates, while ku80 and lig4 mutants displayed moderate increases. Ku80 mutant strains also contained extended single-stranded 3' telomeric overhangs. We concluded that NHEJ proteins have multiple roles at telomeres, mediating fusions of mutant telomeres and ensuring end protection of normal telomeres.
Figures
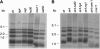
Similar articles
-
Genetic dissection of the Kluyveromyces lactis telomere and evidence for telomere capping defects in TER1 mutants with long telomeres.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Apr;3(2):369-84. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.2.369-384.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15075267 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase, the recombination machinery and Rap1 play redundant roles in yeast telomere protection.Curr Genet. 2021 Feb;67(1):153-163. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01125-4. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33156376
-
Factors influencing the recombinational expansion and spread of telomeric tandem arrays in Kluyveromyces lactis.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Oct;2(5):1115-27. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.5.1115-1127.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 14555494 Free PMC article.
-
Tying up loose ends: nonhomologous end-joining in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mutat Res. 2000 Jun 30;451(1-2):71-89. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(00)00041-5. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10915866 Review.
-
The role of the nonhomologous end-joining DNA double-strand break repair pathway in telomere biology.Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:237-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.110304.095755. Annu Rev Genet. 2006. PMID: 16822175 Review.
Cited by
-
End joining at Caenorhabditis elegans telomeres.Genetics. 2008 Oct;180(2):741-54. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.089920. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18780750 Free PMC article.
-
The Candida albicans Ku70 modulates telomere length and structure by regulating both telomerase and recombination.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023732. Epub 2011 Aug 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21886818 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant telomeric repeats in yeast can disrupt the negative regulation of recombination-mediated telomere maintenance and create an alternative lengthening of telomeres-like phenotype.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):626-39. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00423-08. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19029249 Free PMC article.
-
The 5' arm of Kluyveromyces lactis telomerase RNA is critical for telomerase function.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(6):1875-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01683-07. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18195041 Free PMC article.
-
RNA recognition by the DNA end-binding Ku heterodimer.RNA. 2013 Jun;19(6):841-51. doi: 10.1261/rna.038703.113. Epub 2013 Apr 22. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23610127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

