Combining image features, case descriptions and UMLS concepts to improve retrieval of medical images
- PMID: 17238426
- PMCID: PMC1839585
Combining image features, case descriptions and UMLS concepts to improve retrieval of medical images
Abstract
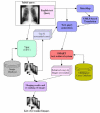
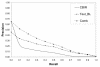
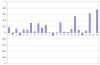
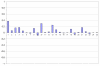
This paper evaluates a system, UBMedTIRS, for retrieval of medical images. The system uses a combination of image and text features as well as mapping of free text to UMLS concepts. UBMedTIRS combines three publicly available tools: a content-based image retrieval system (GIFT), a text retrieval system (SMART), and a tool for mapping free text to UMLS concepts (MetaMap). The system is evaluated using the ImageCLEFmed 2005 collection that contains approximately 50,000 medical images with associated text descriptions in English, French and German. Our experimental results indicate that the proposed approach yields significant improvements in retrieval performance. Our system performs 156% above the GIFT system and 42% above the text retrieval system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automated semantic indexing of figure captions to improve radiology image retrieval.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2009 May-Jun;16(3):380-6. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2945. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19261938 Free PMC article.
-
Document/query expansion based on selecting significant concepts for context based retrieval of medical images.J Biomed Inform. 2019 Jul;95:103210. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103210. Epub 2019 May 17. J Biomed Inform. 2019. PMID: 31108208
-
A normalized lexical lookup approach to identifying UMLS concepts in free text.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2007;129(Pt 1):545-9. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2007. PMID: 17911776
-
The ImageCLEFmed medical image retrieval task test collection.J Digit Imaging. 2009 Dec;22(6):648-55. doi: 10.1007/s10278-008-9154-8. Epub 2008 Sep 3. J Digit Imaging. 2009. PMID: 18769965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical image databases: a content-based retrieval approach.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1997 May-Jun;4(3):184-98. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1997.0040184. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1997. PMID: 9147338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medical Image Retrieval: A Multimodal Approach.Cancer Inform. 2015 Jul 22;13(Suppl 3):125-36. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S14053. eCollection 2014. Cancer Inform. 2015. PMID: 26309389 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical ontologies in action: role in knowledge management, data integration and decision support.Yearb Med Inform. 2008:67-79. Yearb Med Inform. 2008. PMID: 18660879 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating an automatic classification method into the medical image retrieval process.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2008 Nov 6;2008:747-51. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2008. PMID: 18999165 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging medical thesauri and physician feedback for improving medical literature retrieval for case queries.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012 Sep-Oct;19(5):851-8. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000293. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012. PMID: 22437075 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of MetaMap: historical perspective and recent advances.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010 May-Jun;17(3):229-36. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2009.002733. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010. PMID: 20442139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Müller H, Michoux N, Bandon D, Geissbuhler A. A review of content-based image retrieval systems in medicine - clinical benefits and future directions, International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004;73:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Shyu CR, Brodley C, Kak A, Kosaka A, Aisen A, Broderick L. ASSERT: A physician-in-the-loop content-based retrieval system for HRCT image databases. Computer Vision and Image Understanding. 1999;75(1/2):111–132.
-
- Keysers D, Dahmen J, Ney H, Wein BB, Lehmann TM. Statistical framework for model-based image retrieval in medical applications. Journal of Enlectronic Imaging. 2003;12(1):59–68.
-
- Clough P, Müller H, Deselaers T, et al. The CLEF 2005 Cross-Language Image Retrieval Track. In: Peters C, Magni R, editors. Cross Language Evaluation Forum 2005. Vienna, Austria: Springer; 2006.
-
- Ruiz ME, Srikanth M. UB at CLEF2004 Cross Language Medical Image Retrieval; Paper presented at: Fifth Workshop of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum (CLEF 2004), 2005; Bath, England.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical