Timeliness of emergency department diagnoses for syndromic surveillance
- PMID: 17238445
- PMCID: PMC1839358
Timeliness of emergency department diagnoses for syndromic surveillance
Abstract
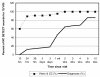
Emergency Department (ED) data are key components of syndromic surveillance systems. While diagnosis data are widely available in electronic form from EDs and have been shown to be an accurate source of clinical data for syndromic surveillance, our previous survey of North Carolina EDs found that the data were not available in a timely manner for early detection. The purpose of this study was to measure the time of availability of participating EDs' diagnosis data in a state-based syndromic surveillance system. We found that a majority of the ED visits transmitted to the state surveillance system for 12/1/05 did not have a diagnosis until more than a week after the visit. Reasons for the lack of timely transmission of diagnoses included coding delays, logistical issues and the lack of IT personnel at smaller hospitals.
Figures
References
-
- Buehler JW, Hopkins RS, Overhage JM, Sosin DM, Tong V. Framework for evaluating public health surveillance systems for early detection of outbreaks. MMWR. 2004;53(RR05):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Heffernan R, Mostashari F, Das D, et al. New York City syndromic surveillance systems. MMWR. 2004;24 (53S):23–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical