A novel phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 17238918
- PMCID: PMC3744940
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05582.x
A novel phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
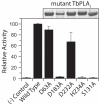
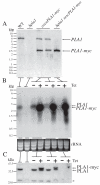
Phospholipase A(1) activities have been detected in most cells where they have been sought and yet their characterization lags far behind that of the phospholipases A(2), C and D. The study presented here details the first cloning and characterization of a cytosolic PLA(1) that exhibits preference for phosphatidylcholine (GPCho) substrates. Trypanosoma brucei phospholipase A(1) (TbPLA(1)) is unique from previously identified eukaryotic PLA(1) because it is evolutionarily related to bacterial secreted PLA(1). A T. brucei ancestor most likely acquired the PLA(1) from a horizontal gene transfer of a PLA(1) from Sodalis glossinidius, a bacterial endosymbiont of tsetse flies. Nano-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry analysis of TbPLA(1) mutants established that the enzyme functions in vivo to synthesize lysoGPCho metabolites containing long-chain mostly polyunsaturated and highly unsaturated fatty acids. Analysis of purified mutated recombinant forms of TbPLA(1) revealed that this enzyme is a serine hydrolase whose catalytic mechanism involves a triad consisting of the amino acid residues Ser-131, His-234 and Asp-183. The TbPLA(1) homozygous null mutants generated here constitute the only PLA(1) double knockouts from any organism.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The role and characterization of phospholipase A1 in mediating lysophosphatidylcholine synthesis in Trypanosoma brucei.Biochem J. 2007 Jul 15;405(2):319-29. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070193. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17402937 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of genetic linkage between heat shock protein 100 and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998 Jul 1;94(1):113-21. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(98)00056-5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998. PMID: 9719514
-
Phospholipase PlaB of Legionella pneumophila represents a novel lipase family: protein residues essential for lipolytic activity, substrate specificity, and hemolysis.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27185-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026021. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19640837 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel cytosolic phospholipase A(2)s, murine cPLA(2){delta}, {epsilon}, and {zeta}, which form a gene cluster with cPLA(2){beta}.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):24576-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413711200. Epub 2005 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15866882
-
The properties and function of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998 Mar 1;91(1):153-64. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(97)00190-4. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998. PMID: 9574933 Review.
Cited by
-
The role and characterization of phospholipase A1 in mediating lysophosphatidylcholine synthesis in Trypanosoma brucei.Biochem J. 2007 Jul 15;405(2):319-29. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070193. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17402937 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis is required for normal mitochondrial morphology and function in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Mar;67(5):1125-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06112.x. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18221265 Free PMC article.
-
The essential neutral sphingomyelinase is involved in the trafficking of the variant surface glycoprotein in the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun;76(6):1461-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07151.x. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20398210 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010 Aug;172(2):66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20382188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipases A₁.Int J Mol Sci. 2011 Jan 18;12(1):588-612. doi: 10.3390/ijms12010588. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21340002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aksoy S, Pourhosseini AA, Chow A. Mycetome endosymbionts of tsetse flies constitute a distinct lineage related to Enterobacteriaceae. Insect Mol Biol. 1995;4:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;604:191–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

