A novel phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 17238918
- PMCID: PMC3744940
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05582.x
A novel phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
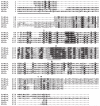
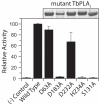
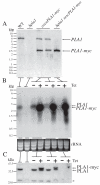
Phospholipase A(1) activities have been detected in most cells where they have been sought and yet their characterization lags far behind that of the phospholipases A(2), C and D. The study presented here details the first cloning and characterization of a cytosolic PLA(1) that exhibits preference for phosphatidylcholine (GPCho) substrates. Trypanosoma brucei phospholipase A(1) (TbPLA(1)) is unique from previously identified eukaryotic PLA(1) because it is evolutionarily related to bacterial secreted PLA(1). A T. brucei ancestor most likely acquired the PLA(1) from a horizontal gene transfer of a PLA(1) from Sodalis glossinidius, a bacterial endosymbiont of tsetse flies. Nano-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry analysis of TbPLA(1) mutants established that the enzyme functions in vivo to synthesize lysoGPCho metabolites containing long-chain mostly polyunsaturated and highly unsaturated fatty acids. Analysis of purified mutated recombinant forms of TbPLA(1) revealed that this enzyme is a serine hydrolase whose catalytic mechanism involves a triad consisting of the amino acid residues Ser-131, His-234 and Asp-183. The TbPLA(1) homozygous null mutants generated here constitute the only PLA(1) double knockouts from any organism.
Figures





References
-
- Aksoy S, Pourhosseini AA, Chow A. Mycetome endosymbionts of tsetse flies constitute a distinct lineage related to Enterobacteriaceae. Insect Mol Biol. 1995;4:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;604:191–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

