Microvesicle-associated tissue factor and Trousseau's syndrome
- PMID: 17239164
- PMCID: PMC3410746
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02301.x
Microvesicle-associated tissue factor and Trousseau's syndrome
Abstract
Background: Trousseau's syndrome is a prothrombotic state associated with malignancy that is poorly understood pathophysiologically.
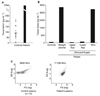
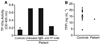
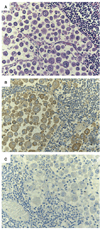
Methods and results: Here we report studies on the blood of a 55-year-old man with giant-cell lung carcinoma who developed a severe form of Trousseau's syndrome. His clinical course was dominated by an extremely hypercoagulable state. Despite receiving potent antithrombotic therapy, he suffered eleven major arterial and venous thrombotic events over a 5 month period. We examined the patient's blood for tissue factor (TF), the major initiator of coagulation, and found its concentration in his plasma to be forty-one-fold higher than the mean concentration derived from testing of 16 normal individuals.
Conclusion: Almost all of the TF in the patient's plasma was associated with cell-derived microvesicles, likely shed by the cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Donati MB. Cancer and thrombosis. Haemostasis. 1994;24:128–131. - PubMed
-
- Trousseau A. Phlegmasia alba dolens. Clinique medicinale de lHotel-Dieu de Paris. London: The New Sydenham Society; 1865.
-
- Bell WR, Starksen NF, Tong S, Porterfield JK. Trousseau’s syndrome. Devastating coagulopathy in the absence of heparin. Am J Med. 1985;79:423–430. - PubMed
-
- Sack GH, Jr, Levin J, Bell WR. Trousseau’s syndrome and other manifestations of chronic disseminated coagulopathy in patients with neoplasms: clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977;56:1–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

