Interleukin-12 and photocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 17239911
- PMCID: PMC2080793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.11.017
Interleukin-12 and photocarcinogenesis
Abstract
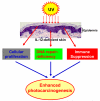
UV radiation induces immunosuppression and inflammatory responses, as well as oxidative stress and DNA damage, in skin cells and these various effects have been implicated in melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers, i.e., photocarcinogenesis. The cytokine interleukin (IL)-12 has been shown to possess potent antitumor activity in a wide variety of murine tumor models. In this review, we summarize the evidence that IL-12 plays a role in preventing photocarcinogenesis, and present a model of its possible mechanisms of action. Treatment of mice with IL-12 prevents UV-induced immunosuppression in a process mediated by repair of UV-induced damaged DNA. After exposure to the photocarcinogenesis protocol, the development of UV-induced tumors is more rapid and the tumor multiplicity and tumor size are significantly greater in IL-12-deficient or knockout (KO) mice than their wild-type counterparts. IL-12-deficiency in mice enhances the proliferation potential of tumor cells, and this may be one of the reasons for the rapid growth of the tumors and their greater size. The rate of malignant transformation of UV-induced papillomas to carcinomas also is higher in the IL-12 KO mice than in their wild-type counterparts in terms of carcinoma incidence and carcinoma multiplicity. UV-induced DNA damage in the form of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and sunburn cells is lower, or repaired more rapidly, in wild-type mice than IL-12 KO mice. The IL-12-associated reduction in UV-specific CPDs is due to induction of DNA repair, and particularly enhancement of nucleotide-excision repair. We suggest that endogenous stimulation of IL-12 may protect the skin from UV-induced immunosuppression, DNA damage, and, ultimately, the risk of photocarcinogenesis. Taken together, this information suggests that augmentation of IL-12 should be considered as a strategy for the prevention and treatment of photocarcinogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-12-deficient mice are at greater risk of UV radiation-induced skin tumors and malignant transformation of papillomas to carcinomas.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Apr;5(4):825-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0003. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16648552
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents photocarcinogenesis in mice through interleukin-12-dependent DNA repair.Cancer Res. 2006 May 15;66(10):5512-20. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0218. Cancer Res. 2006. Retraction in: Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 1;78(23):6709. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3092. PMID: 16707481 Retracted.
-
Prevention of ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in mice is mediated through interleukin 12-dependent DNA repair.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;12(7 Pt 1):2272-80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2672. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16609044
-
Current concept of photocarcinogenesis.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2015 Sep 26;14(9):1713-21. doi: 10.1039/c5pp00185d. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26177397 Review.
-
Photocarcinogenesis of the skin: Current status and future trends.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025 Apr;41(4):e12946. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12946. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39907400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk Among UV-Induced Inflammatory Mediators, DNA Damage and Epigenetic Regulators Facilitates Suppression of the Immune System.Photochem Photobiol. 2017 Jul;93(4):930-936. doi: 10.1111/php.12687. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Photochem Photobiol. 2017. PMID: 27935057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea prevents non-melanoma skin cancer by enhancing DNA repair.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011 Apr 15;508(2):152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.11.015. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21094124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of narrowband ultraviolet B (311 nm) exposure on skin carcinogenesis in Wistar rats.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2024 Dec 29;11(4):1105-1113. doi: 10.5455/javar.2024.k861. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2024. PMID: 40013270 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive grape proanthocyanidins enhance immune reactivity in UV-irradiated skin through functional activation of dendritic cells in mice.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Mar;6(3):242-52. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0320. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23321928 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of endogenous interleukin-12 activates survival signals in ultraviolet-exposed mouse skin and skin tumors.Neoplasia. 2009 Sep;11(9):846-55. doi: 10.1593/neo.09528. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19724678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapman RS, Cooper KD, De Fabo EC, Frederick JE, Gelatt KN, Hammond SP, Hersey P, Koren HS, Ley RD, Noonan F. Solar ultraviolet radiation and the risk of infectious disease. Photochem. Photobiol. 1995;61:223–247. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Chen D, Bloack E, O’Donnell M, Kufe DW, Clinton SK. Eradication of murine bladder carcinoma by intratumor injection of a bicistronic adenoviral vector carrying cDNAs for the IL-12 heterodimer and its inhibition by the p40 subunit homodimer. J. Immunol. 1997;159:351–359. - PubMed
-
- Colombo MP, Vagliani M, Spreafico F, Parenza M, Chiodoni C, Melani C, Stoppacciaro A. Amount of interleukin 12 available at the tumor site is critical for tumor regression. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2531–2534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

