Differential FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910, Ser-843 and Tyr-397 induced by angiotensin II, LPA and EGF in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 17240116
- PMCID: PMC1868572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.11.004
Differential FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910, Ser-843 and Tyr-397 induced by angiotensin II, LPA and EGF in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
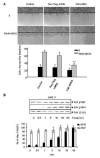
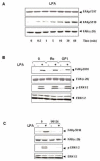
A rapid increase in the tyrosine phosphorylation of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase FAK is a prominent early event in fibroblasts stimulated by a variety of signaling molecules. However, a variety of epithelial cells, including intestinal epithelial cells, show a high basal level of tyrosine phosphorylated FAK that is only slightly further increased by addition of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) agonists or growth factors. In this study, we determined whether these stimuli could elicit FAK phosphorylation at serine residues, including Ser-910 and Ser-843. Our results show that multiple agonists including angiotensin II (ANGII), lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), phorbol esters and EGF induced a striking stimulation of FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910 in rat intestinal epithelial IEC-18 cells via an ERK-dependent pathway. In striking contrast, none of these stimuli promoted a significant further increase in FAK phosphorylation at Tyr-397 in these cells. These results were extended using cultures of polarized human colonic epithelial T84 cells. We found that either carbachol or EGF promoted a striking ERK-dependent phosphorylation of FAK at Ser-910, but these agonists caused only slight stimulation of FAK at Tyr-397 in T84 cells. In addition, we demonstrated that GPCR agonists also induced a dramatic increase of FAK phosphorylation at Ser-843 in either IEC-18 or T84 cells. Our results indicate that Ser-910 and Ser-843, rather than Tyr-397, are prominent sites differentially phosphorylated in response to neurotransmitters, bioactive lipids, tumor promoters and growth factors in intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bombesin, lysophosphatidic acid, and epidermal growth factor rapidly stimulate focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation at Ser-910: requirement for ERK activation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 20;278(25):22631-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210876200. Epub 2003 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12692126
-
PDGF and FGF induce focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation at Ser-910: dissociation from Tyr-397 phosphorylation and requirement for ERK activation.J Cell Physiol. 2004 Aug;200(2):213-22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20018. J Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15174091
-
Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates muscarinic stimulation of focal adhesion kinase in intestinal epithelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Apr;203(1):103-10. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20190. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15389641
-
Mitogenic signaling pathways induced by G protein-coupled receptors.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Dec;213(3):589-602. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21246. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17786953 Review.
-
Importance of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Hormone-Regulated Plant Growth and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 13;23(12):6603. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126603. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743047 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GABAB receptor upregulates fragile X mental retardation protein expression in neurons.Sci Rep. 2015 May 28;5:10468. doi: 10.1038/srep10468. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26020477 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian Cancer Dissemination-A Cell Biologist's Perspective.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 6;11(12):1957. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121957. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling diversity enabled by Rap1-regulated plasma membrane ERK with distinct temporal dynamics.Elife. 2020 May 26;9:e57410. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57410. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32452765 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational dynamics of the focal adhesion targeting domain control specific functions of focal adhesion kinase in cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 2;290(1):478-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.593632. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25391654 Free PMC article.
-
Role of focal adhesion kinase Ser-732 phosphorylation in centrosome function during mitosis.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 3;284(14):9418-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809040200. Epub 2009 Feb 6. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19201755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zachary I, Rozengurt E. Focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK): a point of convergence in the action of neuropeptides, integrins, and oncogenes. Cell. 1992;71:891–894. - PubMed
-
- Rozengurt E. Convergent signalling in the action of integrins, neuropeptides, growth factors and oncogenes. Cancer Surv. 1995;24:81–96. - PubMed
-
- Hanks SK, Polte TR. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Bioessays. 1997;19:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Schlaepfer DD, Hauck CR, Sieg DJ. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999;71:435–478. - PubMed
-
- Schaller MD. Biochemical signals and biological responses elicited by the focal adhesion kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1540:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

