Differential FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910, Ser-843 and Tyr-397 induced by angiotensin II, LPA and EGF in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 17240116
- PMCID: PMC1868572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.11.004
Differential FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910, Ser-843 and Tyr-397 induced by angiotensin II, LPA and EGF in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
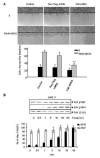
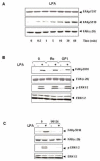
A rapid increase in the tyrosine phosphorylation of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase FAK is a prominent early event in fibroblasts stimulated by a variety of signaling molecules. However, a variety of epithelial cells, including intestinal epithelial cells, show a high basal level of tyrosine phosphorylated FAK that is only slightly further increased by addition of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) agonists or growth factors. In this study, we determined whether these stimuli could elicit FAK phosphorylation at serine residues, including Ser-910 and Ser-843. Our results show that multiple agonists including angiotensin II (ANGII), lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), phorbol esters and EGF induced a striking stimulation of FAK phosphorylation at Ser-910 in rat intestinal epithelial IEC-18 cells via an ERK-dependent pathway. In striking contrast, none of these stimuli promoted a significant further increase in FAK phosphorylation at Tyr-397 in these cells. These results were extended using cultures of polarized human colonic epithelial T84 cells. We found that either carbachol or EGF promoted a striking ERK-dependent phosphorylation of FAK at Ser-910, but these agonists caused only slight stimulation of FAK at Tyr-397 in T84 cells. In addition, we demonstrated that GPCR agonists also induced a dramatic increase of FAK phosphorylation at Ser-843 in either IEC-18 or T84 cells. Our results indicate that Ser-910 and Ser-843, rather than Tyr-397, are prominent sites differentially phosphorylated in response to neurotransmitters, bioactive lipids, tumor promoters and growth factors in intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures





References
-
- Zachary I, Rozengurt E. Focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK): a point of convergence in the action of neuropeptides, integrins, and oncogenes. Cell. 1992;71:891–894. - PubMed
-
- Rozengurt E. Convergent signalling in the action of integrins, neuropeptides, growth factors and oncogenes. Cancer Surv. 1995;24:81–96. - PubMed
-
- Hanks SK, Polte TR. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Bioessays. 1997;19:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Schlaepfer DD, Hauck CR, Sieg DJ. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999;71:435–478. - PubMed
-
- Schaller MD. Biochemical signals and biological responses elicited by the focal adhesion kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1540:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

