Regulation of catalytic activities of HECT ubiquitin ligases
- PMID: 17240353
- PMCID: PMC2563040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.025
Regulation of catalytic activities of HECT ubiquitin ligases
Abstract
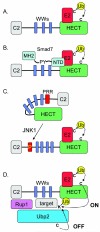
Studies in yeast and mammalian cells over the past decade have shown that HECT domain ubiquitin ligases (HECT E3 enzymes) are involved in diverse physiological pathways. Many substrates of specific HECT E3s have been identified, as well as many adaptor proteins that aid in defining substrate specificity or intra-cellular localization of HECT E3s. Here we review some recently discovered mechanisms for regulation of the catalytic activities of HECT E3s, including regulation at the level of E2 recruitment, phosphorylation-dependent relief of inhibitory intra-molecular interactions, and regulation by association with a deubiquitinating enzyme.
Figures
References
-
- Pickart CM. Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:503–533. - PubMed
-
- Scheffner M, Nuber U, Huibregtse JM. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 1995;373:81–83. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Kinnucan E, Wang G, Beaudenon S, Howley PM, Huibregtse JM, Pavletich NP. Structure of an E6AP-UbcH7 complex: insights into ubiquitination by the E2-E3 enzyme cascade. Science. 1999;286:1321–1326. - PubMed
-
- Ogunjimi AA, Briant DJ, Pece-Barbara N, Le Roy C, Di Guglielmo GM, Kavsak P, Rasmussen RK, Seet BT, Sicheri F, Wrana JL. Regulation of Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase activity by anchoring the E2 to the HECT domain. Mol Cell. 2005;19:297–308. - PubMed
-
- Verdecia MA, Joazeiro CA, Wells NJ, Ferrer JL, Bowman ME, Hunter T, Noel JP. Conformational flexibility underlies ubiquitin ligation mediated by the WWP1 HECT domain E3 ligase. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:249–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

