Translational control of maskin mRNA by its 3' untranslated region
- PMID: 17241108
- PMCID: PMC1888485
- DOI: 10.1042/BC20060112
Translational control of maskin mRNA by its 3' untranslated region
Abstract
Background information: Maskin is a member of the TACC (transforming acidic coiled-coil) domain proteins found in Xenopus laevis oocytes and embryos. It has been implicated in the co-ordination of the spindle and has been reported to mediate translational repression of cyclin B1 mRNA.
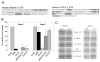
Results: In the present study, we report that maskin mRNA is translationally repressed at the level of initiation in stage 4 oocytes and becomes activated in stage 6 oocytes. The translational repression of maskin mRNA correlates with the presence of a short poly(A) tail on this mRNA in stage 4 oocytes. The 3'-UTR (untranslated region) of maskin can confer the translational regulation to a reporter mRNA, and so can the 3'-UTR of human TACC3. A conserved GUCU repeat element was found to repress translation in both stage 4 and stage 6 oocytes, but deletion of this element did not abrogate repression in stage 4 oocytes. UV cross-linking experiments indicated that overlapping sets of proteins bind efficiently to both the maskin and the cyclin B1 3'-UTRs. As reported previously, CPEB [CPE (cytoplasmic polyadenylation element)-binding protein] binds to the cyclin B1 3'-UTR, but its binding to the maskin 3'-UTR is minimal. By RNA affinity chromatography and MS, we identified the EDEN-BP [EDEN (embryonic deadenylation element)-binding protein] as one of the proteins binding to both the maskin and the cyclin B1 3'-UTRs.
Conclusions: Maskin mRNA is translationally regulated by at least two repressor elements and an activation element. One of the repessor elements is the evolutionarily conserved GUCU repeat. EDEN-BP binds to both the maskin and cyclin B1 3'-UTRs, indicating it may be involved in the deadenylation of these mRNAs.
Figures




References
-
- Albee AJ, Tao W, Wiese C. Phosphorylation of maskin by Aurora-A is regulated by RanGTP and importin beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:38293–38301. - PubMed
-
- Barnard DC, Ryan K, Manley JL, Richter JD. Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Cell. 2004;119:641–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

