Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants QnrA, QnrB, and QnrS among clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae in a Taiwanese hospital
- PMID: 17242140
- PMCID: PMC1855486
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01195-06
Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants QnrA, QnrB, and QnrS among clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae in a Taiwanese hospital
Abstract
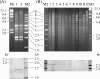
The prevalence of three plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants, QnrA, QnrB, and QnrS, among 526 nonreplicate clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae collected at a Taiwanese university hospital in 2004 was determined by PCR and colony hybridization, and the association of Qnr with the IMP-8 metallo-beta-lactamase was investigated. Eighty-six (16.3%) of all isolates were qnr positive, and the qnrA1-like, qnrB2-like, and qnrS1-like genes were detected alone or in combination in 3 (0.6%), 53 (10.1%), and 34 (6.5%) isolates, respectively. Among 149 putative extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing isolates, 59 (39.6%) isolates, all of which were SHV-12 producers, harbored qnrA (0.7%; 1 isolate), qnrB (28.9%; 43 isolates), or qnrS (12.1%; 18 isolates). Forty-four (78.6%) of 56 IMP-8 producers carried qnrB (58.9%; 33 isolates), qnrS (25.0%; 14 isolates), or both. PCR and sequence analysis revealed that qnrA1 was located in a complex sul1-type integron that contains dhr15, aadA2, qacEDelta1, sul1, orf513, qnrA1, ampR, and qacEDelta1. Conjugation experiments revealed the coexistence of qnrB and bla(IMP-8) on the transferred plasmids and the absence of beta-lactamase content on the transferred qnrS-positive plasmids. The transferred bla(IMP-8)-positive plasmids with and without qnrB had very similar restriction patterns, suggesting the horizontal mobility of qnrB. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis showed six major patterns among the 44 qnr-positive IMP-8-producing isolates. Thus, the extremely high prevalence of qnr among the metallo-beta-lactamase-producing E. cloacae isolates in the hospital may be due mainly to the intrahospital spread of a few clones and the dissemination of plasmids containing both qnrB and blaIMP-8.
Figures
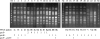
References
-
- Cambau, E., C. Lascols, W. Sougakoff, C. Bebear, R. Bonnet, J. D. Cavallo, L. Gutmann, M. C. Ploy, V. Jarlier, C. J. Soussy, and J. Robert. 2006. Occurrence of qnrA-positive clinical isolates in French teaching hospitals during 2002-2005. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12:1013-1020. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y.-T., H.-Y. Shu, L.-H. Li, T.-L. Liao, K.-M. Wu, Y.-R. Shiau, J.-J. Yan, I.-J. Su, S.-F. Tsai, and T.-L. Lauderdale. 2006. Complete nucleotide sequence of pK245, a 98-kilobase plasmid conferring quinolone resistance and extended-spectrum-β-lactamase activity in a clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:3861-3866. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheung, T. K., Y. W. Chu, M. Y. Chu, C. H. Ma, R. W. Yung, and K. M. Kam. 2005. Plasmid-mediated resistance to ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime in clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis in Hong Kong. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:586-589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

