Chromosome-encoded narrow-spectrum Ambler class A beta-lactamase GIL-1 from Citrobacter gillenii
- PMID: 17242148
- PMCID: PMC1855525
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01152-06
Chromosome-encoded narrow-spectrum Ambler class A beta-lactamase GIL-1 from Citrobacter gillenii
Abstract
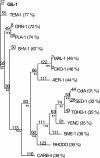
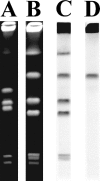
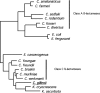
A novel beta-lactamase gene was cloned from the whole-cell DNA of an enterobacterial Citrobacter gillenii reference strain that displayed a weak narrow-spectrum beta-lactam-resistant phenotype and was expressed in Escherichia coli. It encoded a clavulanic acid-inhibited Ambler class A beta-lactamase, GIL-1, with a pI value of 7.5 and a molecular mass of ca. 29 kDa. GIL-1 had the highest percent amino acid sequence identity with TEM-1 and SHV-1, 77%, and 67%, respectively, and only 46%, 31%, and 32% amino acid sequence identity with CKO-1 (C. koseri), CdiA1 (C. diversus), and SED-1 (C. sedlaki), respectively. The substrate profile of the purified GIL-1 was similar to that of beta-lactamases TEM-1 and SHV-1. The blaGIL-1 gene was chromosomally located, as revealed by I-CeuI experiments, and was constitutively expressed at a low level in C. gillenii. No gene homologous to the regulatory ampR genes of chromosomal class C beta-lactamases was found upstream of the blaGIL-1 gene, which fits the noninducibility of beta-lactamase expression in C. gillenii. Rapid amplification of DNA 5' ends analysis of the promoter region revealed putative promoter sequences that diverge from what has been identified as the consensus sequence in E. coli. The blaGIL-1 gene was part of a 5.5-kb DNA fragment bracketed by a 9-bp duplication and inserted between the d-lactate dehydrogenase gene and the ydbH genes; this DNA fragment was absent in other Citrobacter species. This work further illustrates the heterogeneity of beta-lactamases in Citrobacter spp., which may indicate that the variability of Citrobacter species is greater than expected.
Figures


References
-
- Avison, M. B., S. Underwood, A. Okazaki, T. R. Walsh, and P. M. Bennett. 2004. Analysis of AmpC beta-lactamase expression and sequence in biochemically atypical ceftazidime-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from paediatric patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53:584-591. - PubMed
-
- Brenner, D. J., C. M. O'Hara, P. A. Grimont, J. M. Janda, E. Falsen, E. Aldova, E. Ageron, J. Schindler, S. L. Abbott, and A. G. Steigerwalt. 1999. Biochemical identification of Citrobacter species defined by DNA hybridization and description of Citrobacter gillenii sp. nov. (formerly Citrobacter genomospecies 10) and Citrobacter murliniae sp. nov. (formerly Citrobacter genomospecies 11). J. Clin. Microbiol. 37:2619-2624. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brenner, D. J., P. A. D. Grimont, A. G. Stigerwalt, G. R. Fanning, E. Ageron, and C. F. Riddle. 1993. Classification of citrobacteria by DNA hybridization: designation of Citrobacter farmerii sp. nov., Citrobacter youngae sp. nov., Citrobacter braakii sp. nov., Citrobacter werkmanii sp. nov., Citrobacter sedlakii sp. nov., and three unnamed Citrobacter genomespecies. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43:645-658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

