In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of heteroaryl isothiazolones against resistant gram-positive pathogens
- PMID: 17242152
- PMCID: PMC1855488
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01315-06
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of heteroaryl isothiazolones against resistant gram-positive pathogens
Abstract
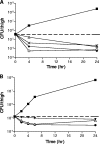
The activities of several tricyclic heteroaryl isothiazolones (HITZs) against an assortment of gram-positive and gram-negative clinical isolates were assessed. These compounds target bacterial DNA replication and were found to possess broad-spectrum activities especially against gram-positive strains, including antibiotic-resistant staphylococci and streptococci. These included methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-nonsusceptible staphylococci, and quinolone-resistant strains. The HITZs were more active than the comparator antimicrobials in most cases. For gram-negative bacteria, the tested compounds were less active against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae but showed exceptional potencies against Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Neisseria spp. Good activity against several anaerobes, as well as Legionella pneumophila and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, was also observed. Excellent bactericidal activity against staphylococci was observed in time-kill assays, with an approximately 3-log drop in the numbers of CFU/ml occurring after 4 h of exposure to compound. Postantibiotic effects (PAEs) of 2.0 and 1.7 h for methicillin-susceptible S. aureus and MRSA strains, respectively, were observed, and these were similar to those seen with moxifloxacin at 10x MIC. In vivo efficacy was demonstrated in murine infections by using sepsis and thigh infection models. The 50% protective doses were <or=1 mg/kg of body weight against S. aureus in the sepsis model, while decreases in the numbers of CFU per thigh equal to or greater than those detected in animals treated with a standard dose of vancomycin were seen in the animals with thigh infections. Pharmacokinetic analyses of treated mice indicated exposures similar to those to ciprofloxacin at equivalent dose levels. These promising initial data suggest further study on the use of the HITZs as antibacterial agents.
Figures

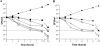
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo profiles of ACH-702, an isothiazoloquinolone, against bacterial pathogens.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Jun;55(6):2860-71. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01666-10. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21464250 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo activities of PD 0305970 and PD 0326448, new bacterial gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitors with potent antibacterial activities versus multidrug-resistant gram-positive and fastidious organism groups.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1191-201. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01321-06. Epub 2007 Jan 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17261623 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative activity of garenoxacin and other agents by susceptibility and time-kill testing against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and respiratory pathogens.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003 Nov;52(5):869-72. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg429. Epub 2003 Sep 30. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003. PMID: 14519672
-
In-vitro profile of a new beta-lactam, ceftobiprole, with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Jun;13 Suppl 2:17-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01722.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17488372 Review.
-
Levonadifloxacin, a Novel Broad-Spectrum Anti-MRSA Benzoquinolizine Quinolone Agent: Review of Current Evidence.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Dec 24;13:4351-4365. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S229882. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31920285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro activity of ACH-702, a new isothiazoloquinolone, against Nocardia brasiliensis compared with econazole and the carbapenems imipenem and meropenem alone or in combination with clavulanic acid.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 May;54(5):2191-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01520-09. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20308390 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo profiles of ACH-702, an isothiazoloquinolone, against bacterial pathogens.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Jun;55(6):2860-71. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01666-10. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21464250 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal activity of ACH-702 against nondividing and biofilm Staphylococci.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jul;56(7):3812-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00092-12. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22547614 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV: target interactions of heteroaryl isothiazolones in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jul;51(7):2445-53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00158-07. Epub 2007 May 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17502409 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges of antibacterial discovery.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jan;24(1):71-109. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00030-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21233508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appelbaum, P. C. 2006. The emergence of vancomycin-intermediate and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12(Suppl. 1):16-23. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Update: Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—United States, 1997. JAMA 278:1145-1146. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2002. Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Pennsylvania, 2002. JAMA 288:2116. - PubMed
-
- Chambers, H. F. 2005. Community-associated MRSA—resistance and virulence converge. N. Engl. J. Med. 352:1485-1487. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

