Developmental changes in histone macroH2A1-mediated gene regulation
- PMID: 17242180
- PMCID: PMC1899912
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02334-06
Developmental changes in histone macroH2A1-mediated gene regulation
Abstract
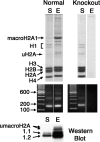
macroH2A histone variants have been implicated to function in gene silencing by several studies, including ones showing a preferential association of macroH2A on the inactive X chromosome. To examine macroH2A function in vivo, we knocked out macroH2A1. macroH2A1 knockout mice are viable and fertile. A broad screen of liver gene expression showed no evidence of defects in X inactivation but did identify genes that have increased expression levels in macroH2A1 knockouts. macroH2A1-containing nucleosomes are enriched on the coding and/or upstream regions of these genes, suggesting that their increased expression levels are a direct effect of the absence of macroH2A1. The concentrations of macroH2A1 nucleosomes on these genes are low in the livers of newborn mice, and the macroH2A1 knockout had little effect on the expression levels of these genes in newborn liver. Our results indicate that an increase in liver macroH2A1 during the transition from newborn to young-adult status contributes to a decrease in the expression levels of these genes. These genes cluster in the area of lipid metabolism, and we observed metabolic effects in macroH2A1 knockouts. Our results indicate that the function of macroH2A1 histones is not restricted to gene silencing but also involves fine tuning the expression of specific genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
macroH2A1 histone variants are depleted on active genes but concentrated on the inactive X chromosome.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;26(12):4410-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02258-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16738309 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide distribution of macroH2A1 histone variants in mouse liver chromatin.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;30(23):5473-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00518-10. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20937776 Free PMC article.
-
Mice without macroH2A histone variants.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;34(24):4523-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00794-14. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25312643 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution, structure and function of divergent macroH2A1 splice isoforms.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 15;135:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.03.036. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35422391 Review.
-
Multiple facets of the unique histone variant macroH2A: from genomics to cell biology.Cell Cycle. 2010 Jul 1;9(13):2568-74. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.13.12144. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20543561 Review.
Cited by
-
MacroH2A1 Immunoexpression in Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 21;10:1519. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01519. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974186 Free PMC article.
-
Is histone acetylation the most important physiological function for CBP and p300?Aging (Albany NY). 2012 Apr;4(4):247-55. doi: 10.18632/aging.100453. Aging (Albany NY). 2012. PMID: 22511639 Free PMC article.
-
MacroH2A histone variants act as a barrier upon reprogramming towards pluripotency.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1565. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2582. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23463008 Free PMC article.
-
Synergism between DNA methylation and macroH2A1 occupancy in epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor gene p16(CDKN2A).Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Mar;39(4):1326-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq994. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21030442 Free PMC article.
-
The macro domain protein family: structure, functions, and their potential therapeutic implications.Mutat Res. 2011 May-Jun;727(3):86-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Mutat Res. 2011. PMID: 21421074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott, D. W., M. Laszczak, J. D. Lewis, H. Su, S. C. Moore, M. Hills, S. Dimitrov, and J. Ausio. 2004. Structural characterization of macroH2A containing chromatin. Biochemistry 43:1352-1359. - PubMed
-
- Allen, M. D., A. M. Buckle, S. C. Cordell, J. Lowe, and M. Bycroft. 2003. The crystal structure of AF1521 a protein from Archaeoglobus fulgidus with homology to the non-histone domain of macroH2A. J. Mol. Biol. 330:503-511. - PubMed
-
- Chadwick, B. P., and H. F. Willard. 2001. Histone H2A variants and the inactive X chromosome: identification of a second macroH2A variant. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10:1101-1113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
