The Myc transactivation domain promotes global phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain independently of direct DNA binding
- PMID: 17242204
- PMCID: PMC1820498
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01828-06
The Myc transactivation domain promotes global phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain independently of direct DNA binding
Abstract
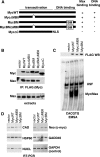
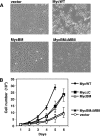
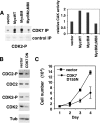
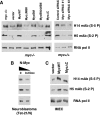
Myc is a transcription factor which is dependent on its DNA binding domain for transcriptional regulation of target genes. Here, we report the surprising finding that Myc mutants devoid of direct DNA binding activity and Myc target gene regulation can rescue a substantial fraction of the growth defect in myc(-/-) fibroblasts. Expression of the Myc transactivation domain alone induces a transcription-independent elevation of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) C-terminal domain (CTD) kinases cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) and CDK9 and a global increase in CTD phosphorylation. The Myc transactivation domain binds to the transcription initiation sites of these promoters and stimulates TFIIH binding in an MBII-dependent manner. Expression of the Myc transactivation domain increases CDK mRNA cap methylation, polysome loading, and the rate of translation. We find that some traditional Myc transcriptional target genes are also regulated by this Myc-driven translation mechanism. We propose that Myc transactivation domain-driven RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation has broad effects on both transcription and mRNA metabolism.
Figures





Similar articles
-
TFIIH-associated Cdk7 kinase functions in phosphorylation of C-terminal domain Ser7 residues, promoter-proximal pausing, and termination by RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;29(20):5455-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00637-09. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19667075 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-separation mechanism for C-terminal hyperphosphorylation of RNA polymerase II.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7709):318-323. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0174-3. Epub 2018 May 30. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29849146 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Tat-associated RNA polymerase C-terminal domain kinase, CDK2, phosphorylates CDK7 and stimulates Tat-mediated transcription.Biochem J. 2002 Jun 15;364(Pt 3):649-57. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011191. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12049628 Free PMC article.
-
Pause, play, repeat: CDKs push RNAP II's buttons.Transcription. 2013 Jul-Aug;4(4):146-52. doi: 10.4161/trns.25146. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23756342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated requirement of non-specific and sequence-specific DNA binding in Myc-driven transcription.EMBO J. 2021 May 17;40(10):e105464. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105464. Epub 2021 Apr 1. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33792944 Free PMC article.
-
Myc transcription factors: key regulators behind establishment and maintenance of pluripotency.Regen Med. 2010 Nov;5(6):947-59. doi: 10.2217/rme.10.79. Regen Med. 2010. PMID: 21082893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MYC Oncogene Contributions to Release of Cell Cycle Brakes.Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 22;10(3):244. doi: 10.3390/genes10030244. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myc and mRNA capping.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1849(5):501-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24681440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-Myc deregulation induces mRNA capping enzyme dependency.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82273-82288. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12701. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27756891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikary, S., F. Marinoni, A. Hock, E. Hulleman, N. Popov, R. Beier, S. Bernard, M. Quarto, M. Capra, S. Goettig, U. Kogel, M. Scheffner, K. Helin, and M. Eilers. 2005. The ubiquitin ligase HectH9 regulates transcriptional activation by Myc and is essential for tumor cell proliferation. Cell 123:409-421. - PubMed
-
- Arabi, A., S. Wu, K. Ridderstrale, H. Bierhoff, C. Shiue, K. Fatyol, S. Fahlen, P. Hydbring, O. Soderberg, I. Grummt, L. G. Larsson, and A. P. Wright. 2005. c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:303-310. - PubMed
-
- Armelin, H. A., M. C. Armelin, K. Kelly, T. Stewart, P. Leder, B. H. Cochran, and C. D. Stiles. 1984. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature 10:55-660. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, D. L. 2005. Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17:251-256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
