Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression
- PMID: 17242205
- PMCID: PMC1820501
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02005-06
Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression
Abstract
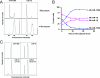
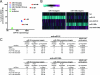
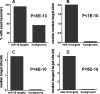
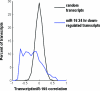
microRNAs (miRNAs) are abundant, approximately 21-nucleotide, noncoding regulatory RNAs. Each miRNA may regulate hundreds of mRNA targets, but the identities of these targets and the processes they regulate are poorly understood. Here we have explored the use of microarray profiling and functional screening to identify targets and biological processes triggered by the transfection of human cells with miRNAs. We demonstrate that a family of miRNAs sharing sequence identity with miRNA-16 (miR-16) negatively regulates cellular growth and cell cycle progression. miR-16-down-regulated transcripts were enriched with genes whose silencing by small interfering RNAs causes an accumulation of cells in G(0)/G(1). Simultaneous silencing of these genes was more effective at blocking cell cycle progression than disruption of the individual genes. Thus, miR-16 coordinately regulates targets that may act in concert to control cell cycle progression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coordinated regulation of cell cycle transcripts by p53-Inducible microRNAs, miR-192 and miR-215.Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 15;68(24):10105-12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1846. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19074876
-
MicroRNA-34b and MicroRNA-34c are targets of p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and adhesion-independent growth.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8433-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1585. Epub 2007 Sep 6. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17823410
-
Target identification of microRNAs expressed highly in human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Apr 15;106(6):1020-30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22084. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19229866
-
[Cellular function of microRNA-15 family].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2012 Feb 25;64(1):101-6. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22348968 Review. Chinese.
-
MicroRNAs and cell cycle regulation.Cell Cycle. 2007 Sep 1;6(17):2127-32. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.17.4641. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17786041 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights about MYC and Apoptosis in B-Lymphomagenesis: An Update from Murine Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4265. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124265. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-16 promotes the apoptosis of human cancer cells by targeting FEAT.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jun 2;15:448. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1458-8. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26031775 Free PMC article.
-
Direct targeting of HGF by miR-16 regulates proliferation and migration in gastric cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):15175-15183. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5390-6. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27683052
-
Perspectives in cell cycle regulation: lessons from an anoxic vertebrate.Curr Genomics. 2009 Dec;10(8):573-84. doi: 10.2174/138920209789503905. Curr Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20514219 Free PMC article.
-
Desperately seeking microRNA targets.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1169-74. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1921. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924405 Review.
References
-
- Ambros, V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350-355. - PubMed
-
- Bagga, S., J. Bracht, S. Hunter, K. Massirer, J. Holtz, R. Eachus, and A. E. Pasquinelli. 2005. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122:553-563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D. P., and C. Z. Chen. 2004. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5:396-400. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich, I. 2005. Prediction and validation of microRNAs and their targets. FEBS Lett. 579:5904-5910. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich, I., A. Avniel, Y. Karov, R. Aharonov, S. Gilad, O. Barad, A. Barzilai, P. Einat, U. Einav, E. Meiri, E. Sharon, Y. Spector, and Z. Bentwich. 2005. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 37:766-770. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
